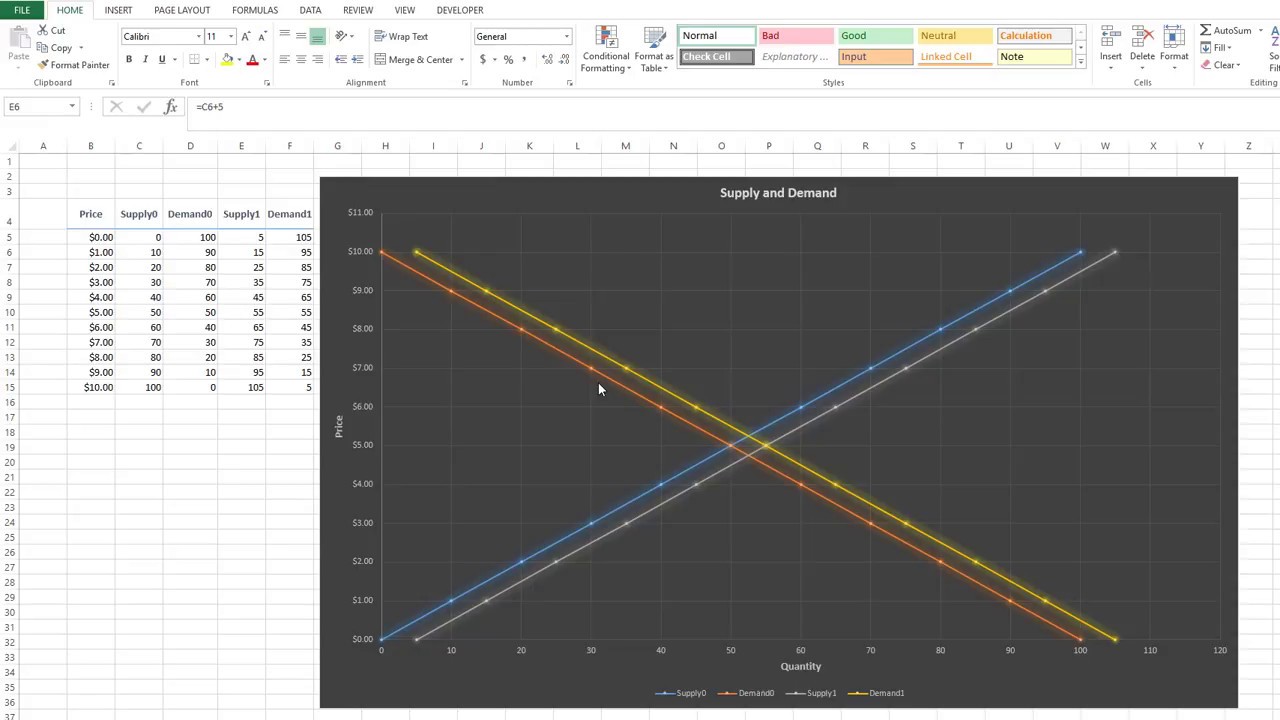
Understanding the supply and demand curve is crucial in economics, as it helps to analyze the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that suppliers are willing to supply and buyers are willing to purchase. Plotting a supply and demand curve in Excel can be a great way to visualize this relationship. Here, we will walk through the 5 easy steps to plot a supply and demand curve in Excel.
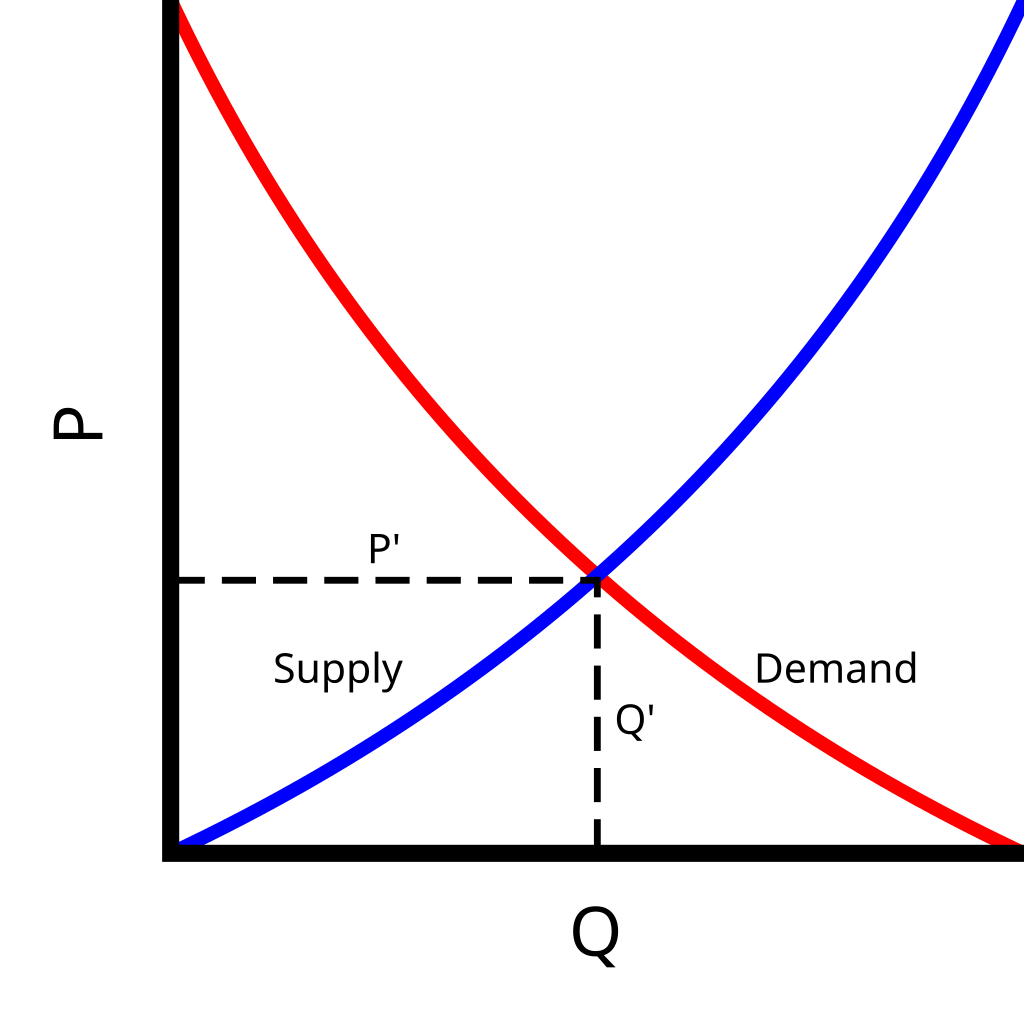
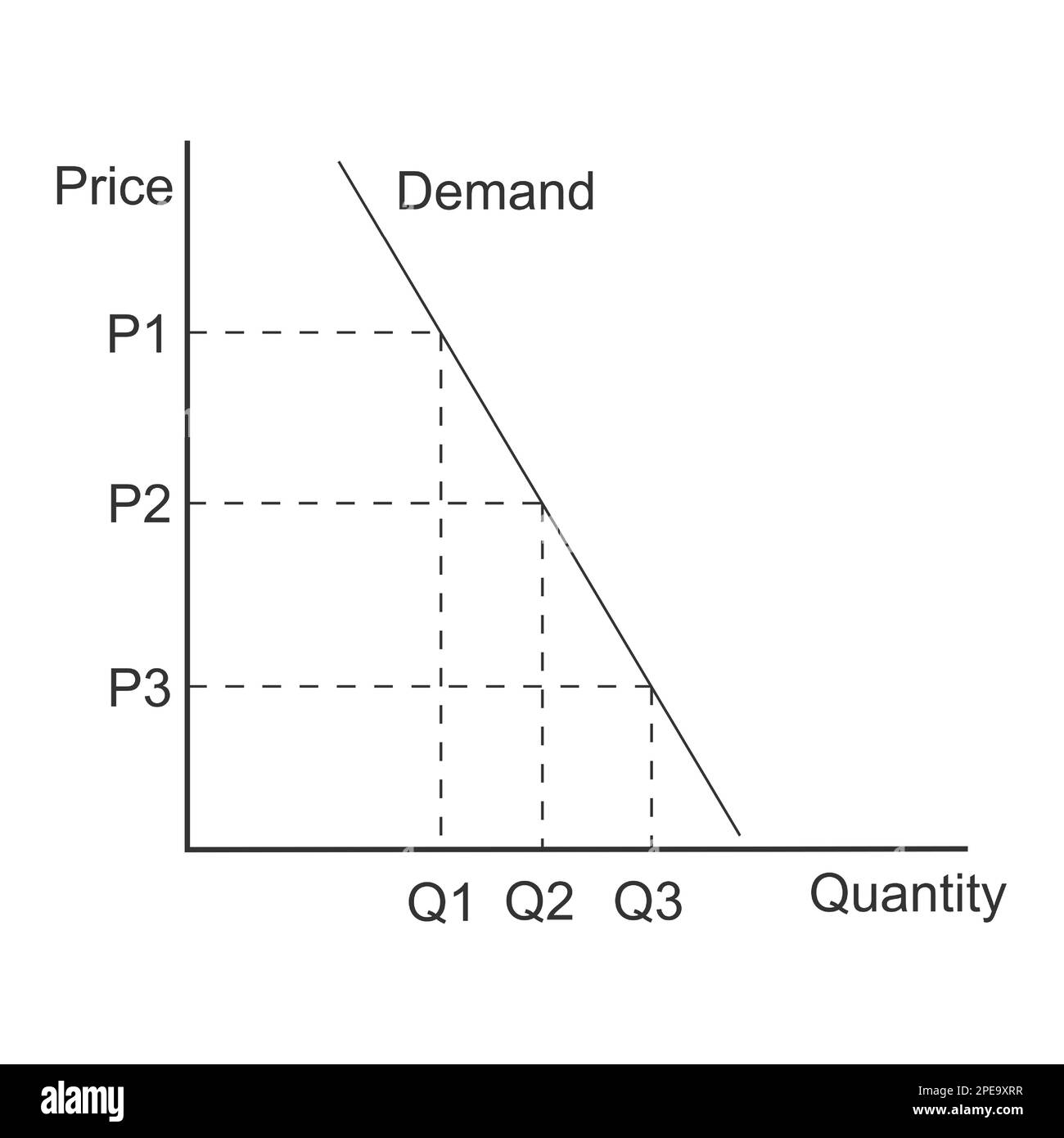
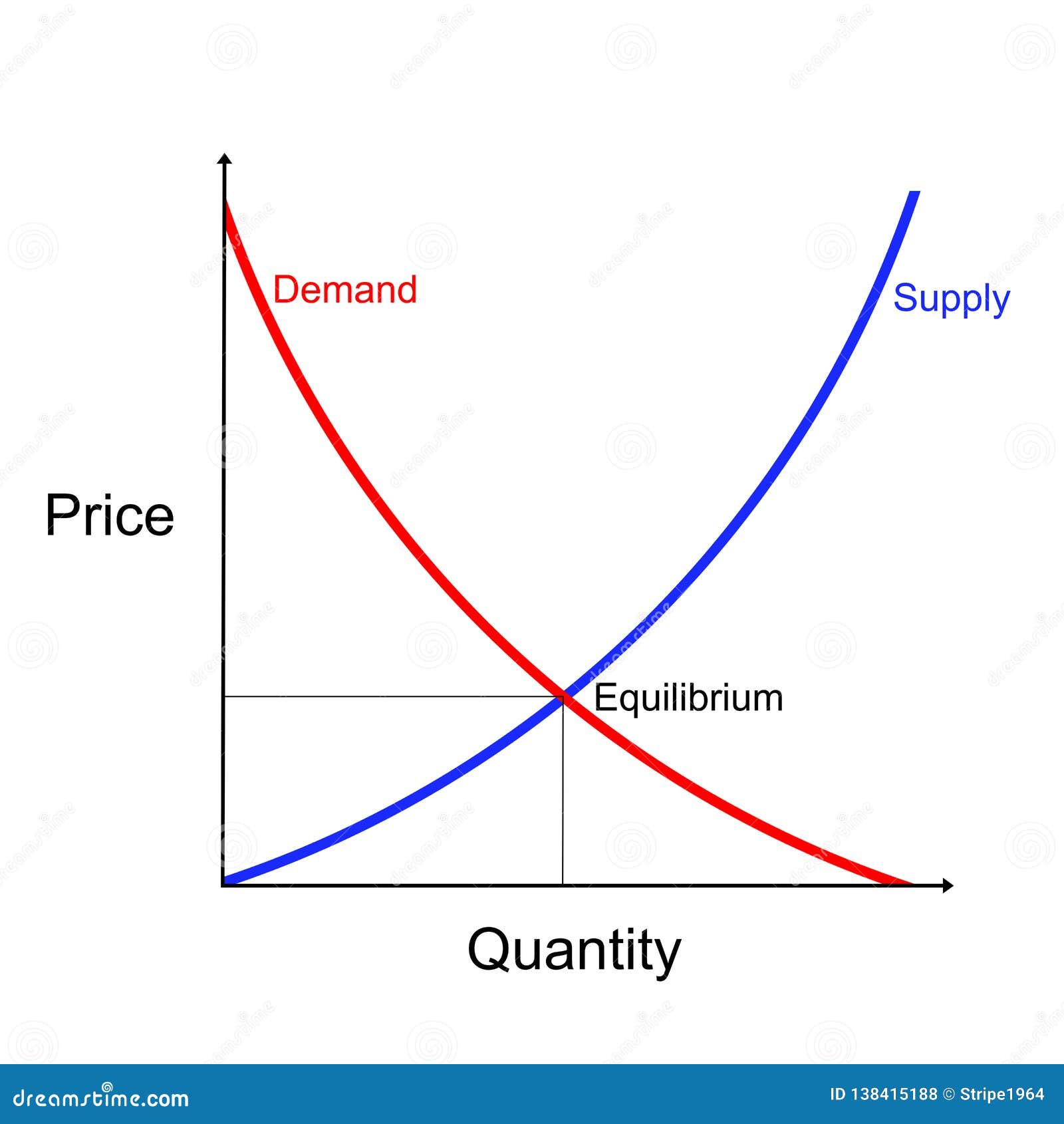
The supply and demand curve is a fundamental concept in economics that helps to determine the price and quantity of a product in a market. The supply curve shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that suppliers are willing to supply, while the demand curve shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that buyers are willing to purchase.
Step 1: Set Up Your Data
To plot a supply and demand curve in Excel, you need to set up your data first. Create a table with three columns: Price, Quantity Supplied, and Quantity Demanded. Enter the data for the price and quantity supplied, and quantity demanded.
For example:
| Price | Quantity Supplied | Quantity Demanded |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 100 | 200 |
| 12 | 120 | 180 |
| 15 | 150 | 150 |
| 18 | 180 | 120 |
| 20 | 200 | 100 |
Step 2: Create a Chart
To create a chart, go to the "Insert" tab in Excel and click on "Chart". Select the "Line" chart and click "OK".
Step 3: Add Data to the Chart
Add the data to the chart by clicking on the "Select Data" button. Select the data range for the quantity supplied and quantity demanded.

Step 4: Customize the Chart
Customize the chart by adding a title, labels, and a legend. You can also change the colors and format of the chart.

Step 5: Analyze the Curve
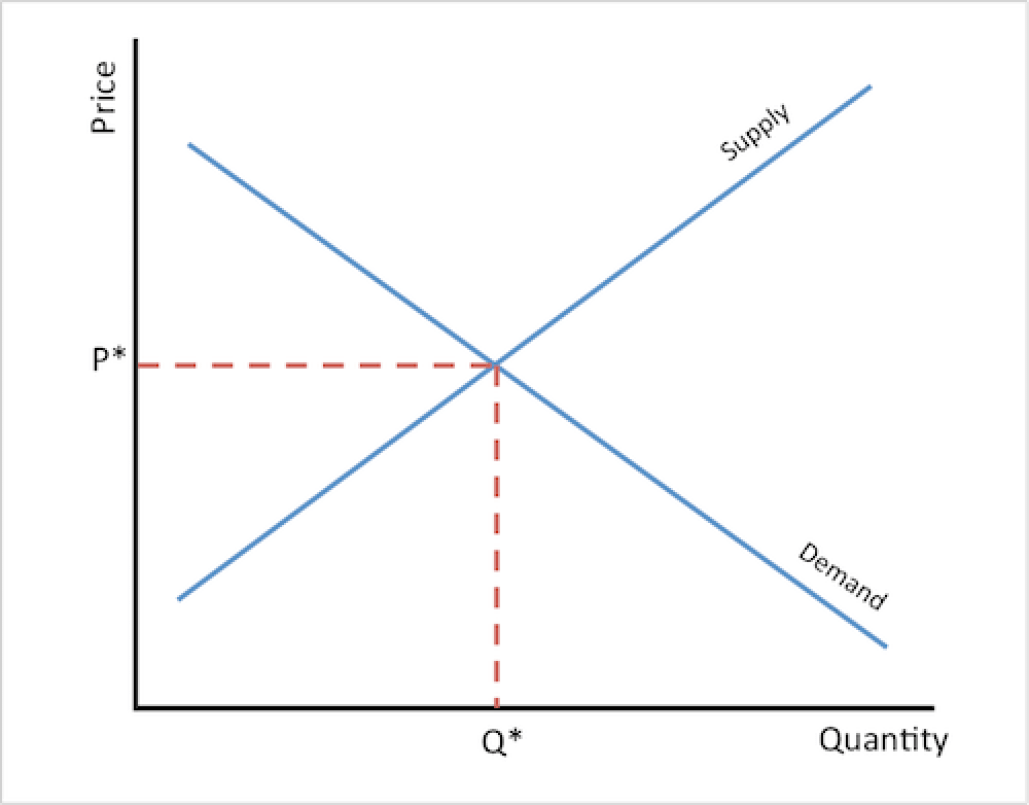
Analyze the curve by looking at the point where the supply and demand curves intersect. This point is called the equilibrium price and quantity.
Benefits of Plotting a Supply and Demand Curve in Excel
Plotting a supply and demand curve in Excel has several benefits, including:
- Visual representation: A supply and demand curve provides a visual representation of the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that suppliers are willing to supply and buyers are willing to purchase.
- Easy to analyze: The curve is easy to analyze and understand, making it a great tool for students and professionals.
- Accurate predictions: The curve can be used to make accurate predictions about the price and quantity of a product in a market.
- Flexibility: Excel allows you to easily change the data and see how it affects the curve.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Plotting a Supply and Demand Curve in Excel
When plotting a supply and demand curve in Excel, there are several common mistakes to avoid, including:
- Incorrect data: Make sure to enter the correct data for the price and quantity supplied and demanded.
- Incorrect chart type: Make sure to select the correct chart type, such as a line chart.
- Incorrect axis labels: Make sure to label the axes correctly, such as price on the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis.
Gallery of Supply and Demand Curve
What is the supply and demand curve?
+The supply and demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that suppliers are willing to supply and buyers are willing to purchase.
How do I plot a supply and demand curve in Excel?
+To plot a supply and demand curve in Excel, follow these steps: set up your data, create a chart, add data to the chart, customize the chart, and analyze the curve.
What are the benefits of plotting a supply and demand curve in Excel?
+The benefits of plotting a supply and demand curve in Excel include a visual representation of the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that suppliers are willing to supply and buyers are willing to purchase, easy to analyze, accurate predictions, and flexibility.
We hope this article has helped you to understand how to plot a supply and demand curve in Excel. With these 5 easy steps, you can create a professional-looking chart that helps you to analyze the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that suppliers are willing to supply and buyers are willing to purchase.