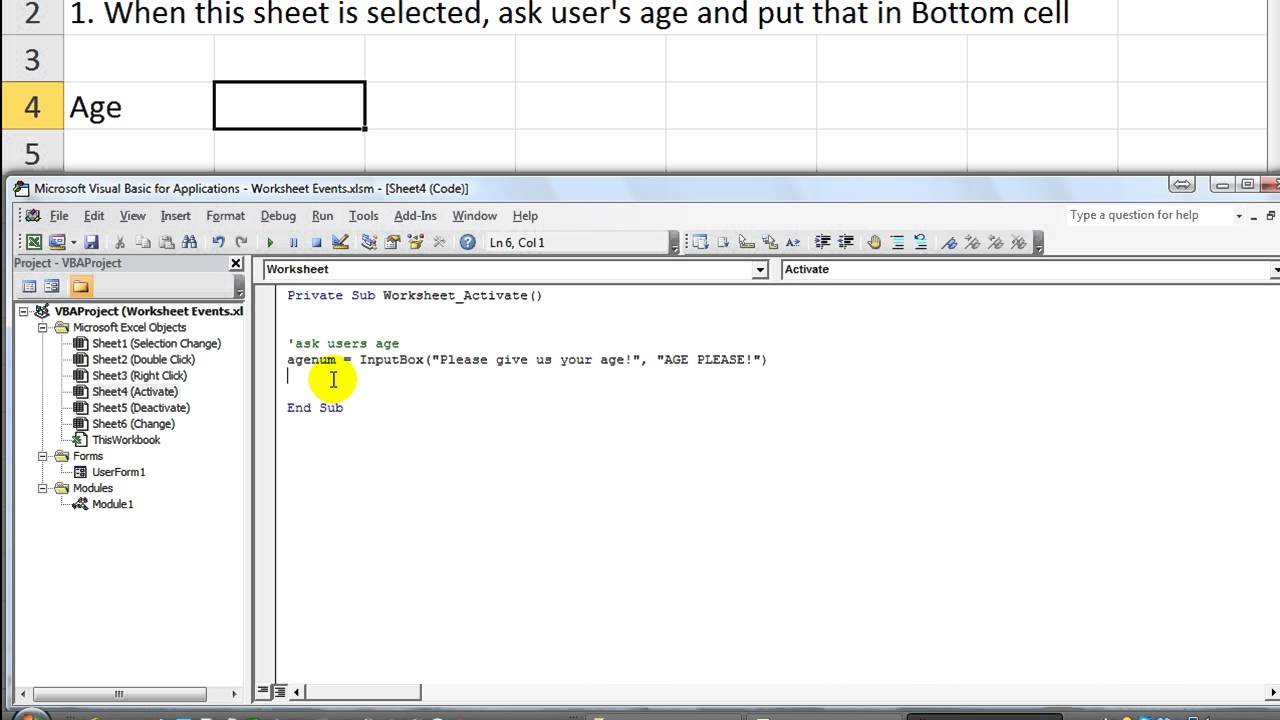
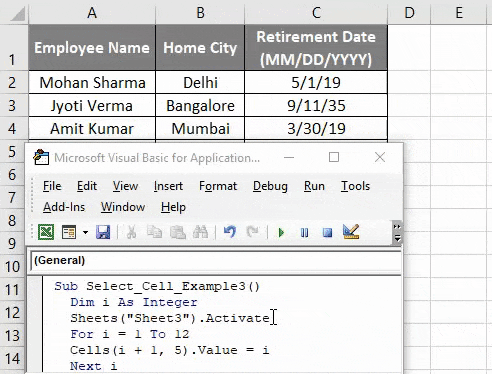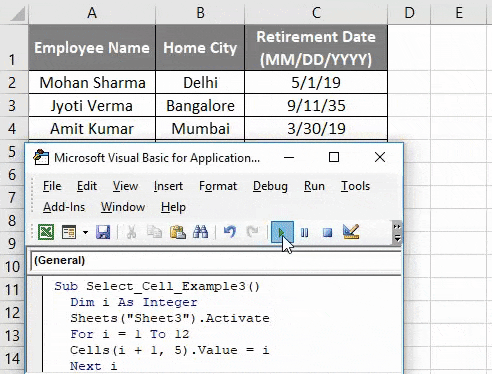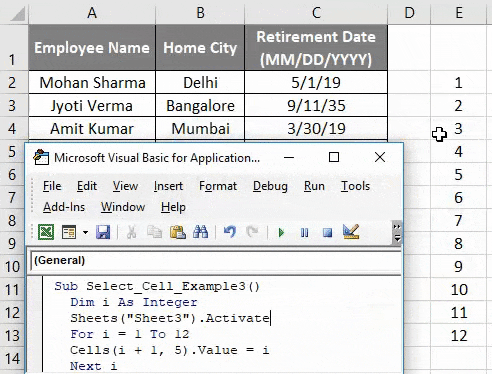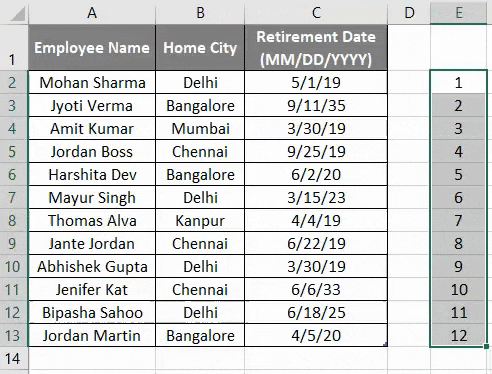
The ability to select sheets in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a fundamental skill for anyone working with Excel macros. Selecting a sheet allows you to perform various actions on that specific sheet, such as formatting, data manipulation, or inserting charts. In this article, we will explore five different ways to select a sheet in VBA, each with its own set of use cases and benefits.
Why is selecting a sheet in VBA important?
Selecting a sheet in VBA is crucial because it allows you to target a specific sheet in your workbook and perform actions on it. Without selecting a sheet, your macro may end up modifying the wrong sheet or even the entire workbook. By selecting a sheet, you can ensure that your macro is working on the correct data and avoiding any potential errors.
Method 1: Using the Sheets Collection
The Sheets collection is a built-in VBA collection that contains all the sheets in a workbook. You can use the Sheets collection to select a sheet by its index or name.
Sub SelectSheetUsingSheetsCollection()
' Select a sheet by its index
Sheets(1).Select
' Select a sheet by its name
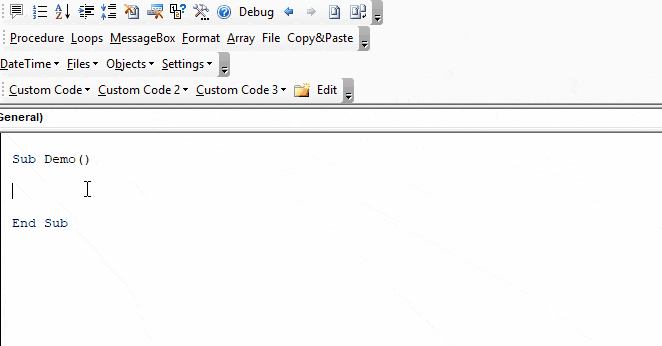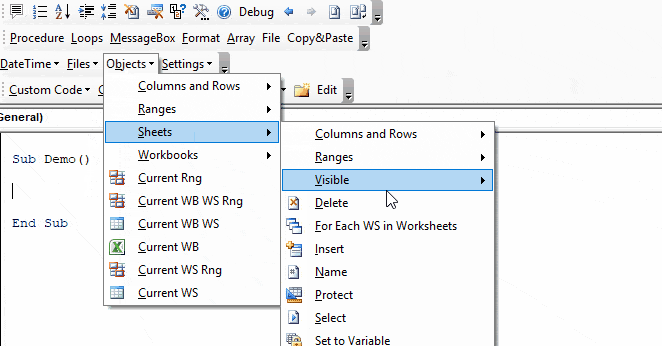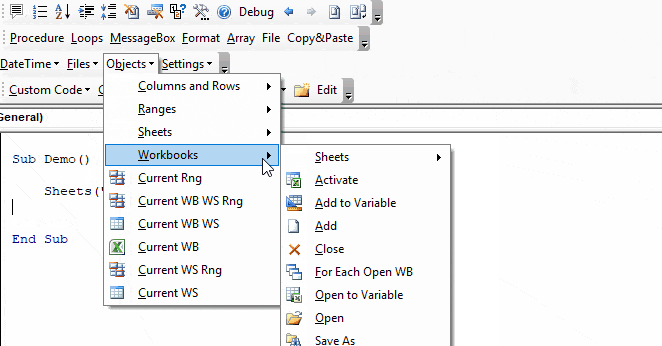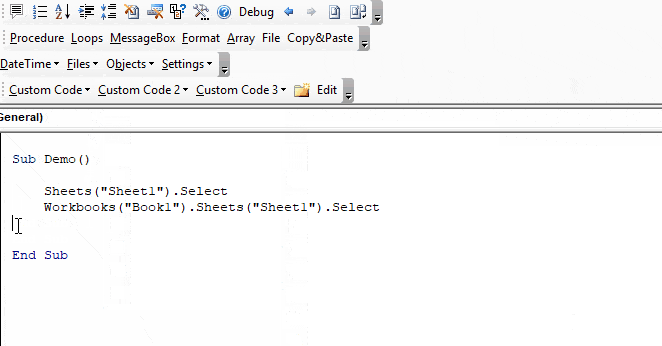
Sheets("Sheet1").Select
End Sub
In the above code, we use the Sheets collection to select the first sheet in the workbook by its index (1) and then select a sheet by its name ("Sheet1").
Method 2: Using the Worksheets Collection
The Worksheets collection is similar to the Sheets collection, but it only contains worksheets, excluding chart sheets and other types of sheets.
Sub SelectSheetUsingWorksheetsCollection()
' Select a worksheet by its index
Worksheets(1).Select
' Select a worksheet by its name
Worksheets("Sheet1").Select
End Sub
In the above code, we use the Worksheets collection to select the first worksheet in the workbook by its index (1) and then select a worksheet by its name ("Sheet1").
Method 3: Using the ActiveSheet Property
The ActiveSheet property returns the currently active sheet in the workbook. You can use this property to select the active sheet.
Sub SelectActiveSheet()
ActiveSheet.Select
End Sub
In the above code, we use the ActiveSheet property to select the currently active sheet.
Method 4: Using the Range Object
You can also select a sheet by selecting a range on that sheet.
Sub SelectSheetUsingRange()
Range("A1").Select
End Sub
In the above code, we select cell A1 on the active sheet, which effectively selects the sheet.
Method 5: Using the Worksheet Object
You can also select a sheet by declaring a Worksheet object and setting it to the desired sheet.
Sub SelectSheetUsingWorksheetObject()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
ws.Select
End Sub
In the above code, we declare a Worksheet object ws and set it to the worksheet named "Sheet1" in the current workbook. We then select the worksheet using the Select method.

Gallery of Selecting Sheets in VBA




FAQs
What is the difference between the `Sheets` and `Worksheets` collections?
+The `Sheets` collection contains all sheets in a workbook, including worksheets, chart sheets, and other types of sheets. The `Worksheets` collection only contains worksheets, excluding chart sheets and other types of sheets.
How do I select a sheet by its name?
+You can select a sheet by its name using the `Sheets` or `Worksheets` collection, like this: `Sheets("Sheet1").Select` or `Worksheets("Sheet1").Select`.
What is the `ActiveSheet` property?
+The `ActiveSheet` property returns the currently active sheet in the workbook. You can use this property to select the active sheet, like this: `ActiveSheet.Select`.
In conclusion, selecting a sheet in VBA is a crucial skill for anyone working with Excel macros. We have explored five different ways to select a sheet, each with its own set of use cases and benefits. By mastering these methods, you can ensure that your macros are working on the correct data and avoiding any potential errors.