The world of Excel can be overwhelming, especially when dealing with large datasets. One common challenge users face is managing columns, which can make or break the overall user experience. Hiding columns in Excel with VBA is a game-changer, and we're here to break it down in simple terms.
Excel is an incredibly powerful tool, but its true potential is unleashed when paired with VBA (Visual Basic for Applications). VBA is a programming language that allows users to automate tasks, create custom tools, and even interact with other Office applications. In this article, we'll delve into the world of VBA and explore how to hide columns in Excel with ease.
Why Hide Columns in Excel?
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let's discuss why hiding columns is essential in Excel. Here are a few reasons:
- Data organization: Hiding columns helps keep your data organized, making it easier to focus on the information that matters.
- Reducing clutter: By hiding unnecessary columns, you can declutter your worksheet and improve its overall appearance.
- Protecting sensitive data: Hiding columns can be a simple way to protect sensitive information, such as employee salaries or confidential client data.
Getting Started with VBA
To hide columns in Excel with VBA, you'll need to access the Visual Basic Editor. Here's how:
- Open your Excel workbook and press
Alt + F11or navigate toDeveloper>Visual Basicin the ribbon. - In the Visual Basic Editor, click
Insert>Moduleto create a new module. - Paste the VBA code into the module.
Basic VBA Code to Hide Columns
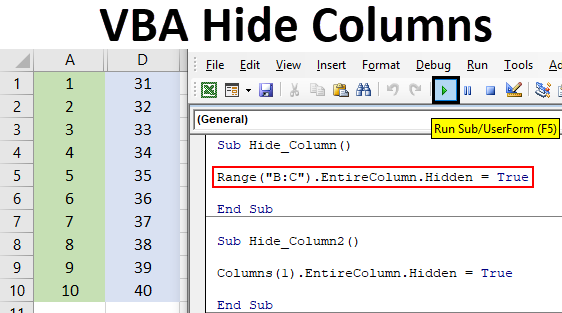
Here's a simple VBA code snippet that hides a single column:
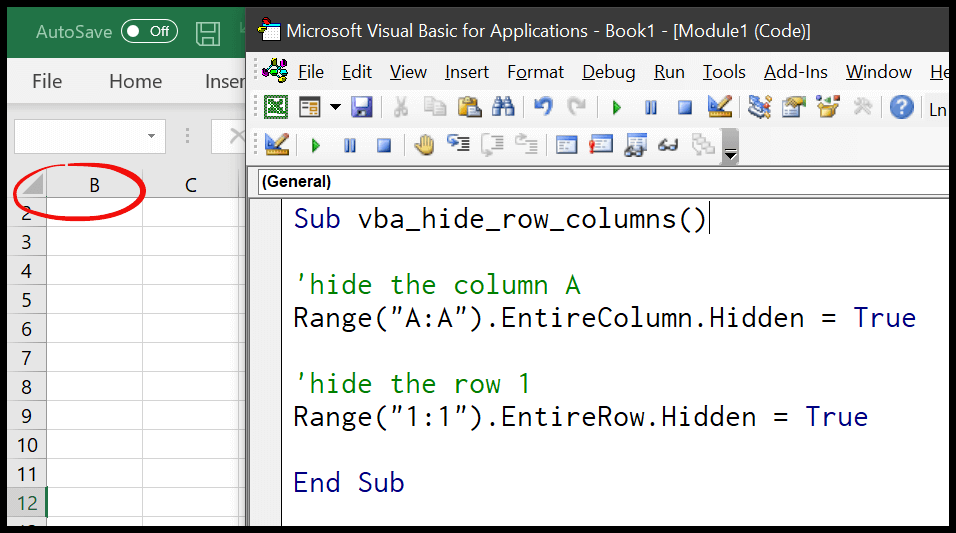
Sub HideColumn()
Columns("A").Hidden = True
End Sub
In this example, replace "A" with the column letter you want to hide. To hide multiple columns, separate the column letters with commas:
Sub HideColumns()
Columns("A, C, E").Hidden = True
End Sub
Dynamic VBA Code to Hide Columns
What if you want to hide columns dynamically based on certain conditions? Here's an example code that hides columns based on the value in a specific cell:
Sub HideColumnsBasedOnValue()
If Range("B2").Value = "Hide" Then
Columns("A:C").Hidden = True
Else
Columns("A:C").Hidden = False
End If
End Sub
In this example, the code checks the value in cell B2. If the value is "Hide", it hides columns A:C. Otherwise, it unhides them.
Tips and Variations
- To unhide columns, set the
Hiddenproperty toFalse. - To hide rows, use the
Rowsobject instead ofColumns. - To hide entire worksheets, use the
Worksheetsobject and set theVisibleproperty toFalse. - To create a toggle button that hides and unhides columns, use the
Worksheet_Changeevent and modify the code accordingly.

Real-World Applications
Hiding columns in Excel with VBA has numerous real-world applications:
- Data analysis: Hide columns that contain intermediate calculations or raw data to focus on the final results.
- Reporting: Hide columns that contain sensitive or confidential information to create reports that can be shared with stakeholders.
- Dashboard creation: Hide columns that contain data that's not relevant to the dashboard's purpose, making it more visually appealing and user-friendly.
Conclusion
Hiding columns in Excel with VBA is a powerful technique that can enhance your workflow, improve data organization, and protect sensitive information. By mastering VBA code and understanding the basics of column hiding, you'll become more efficient and proficient in your Excel endeavors.
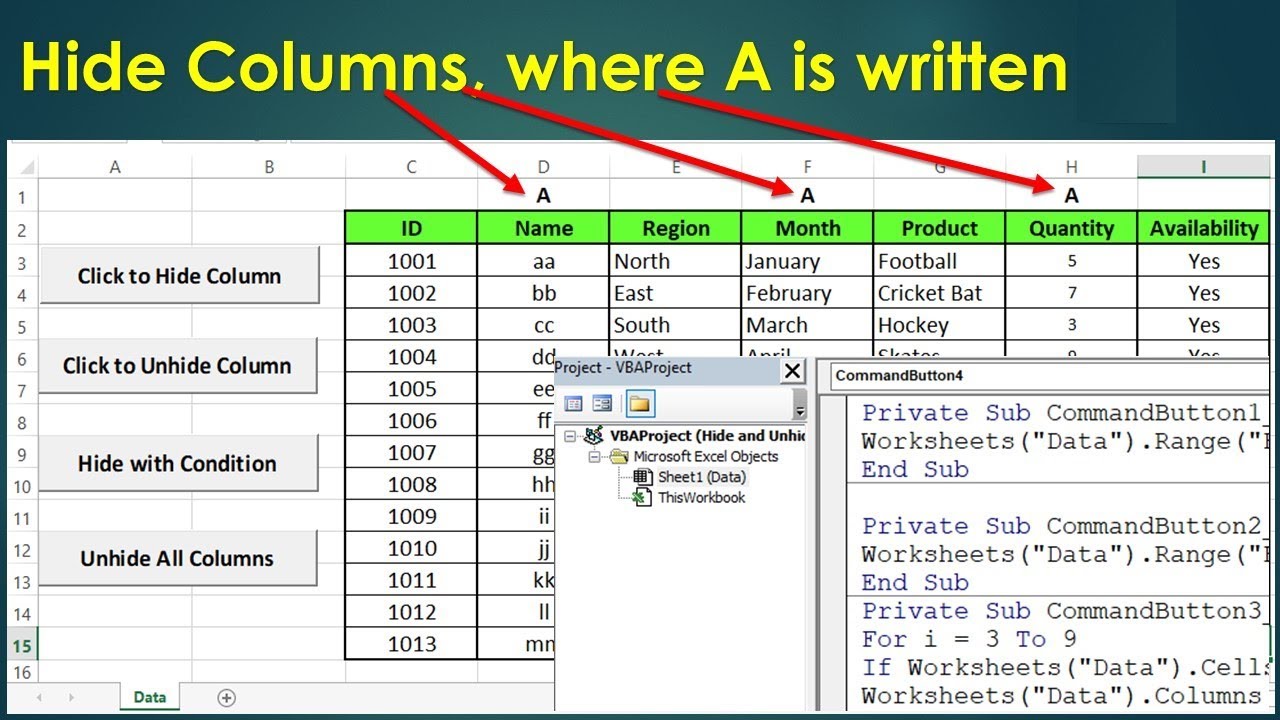
Gallery of Excel VBA Column Hiding Examples




Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between hiding and unhiding columns in Excel?
+Hiding columns makes them invisible, while unhiding columns makes them visible again. Hiding columns does not delete the data, but rather hides it from view.
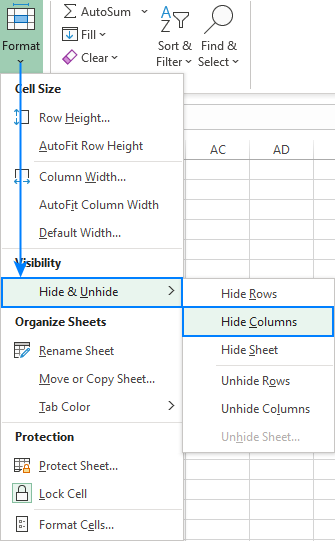
Can I hide columns in Excel without using VBA?
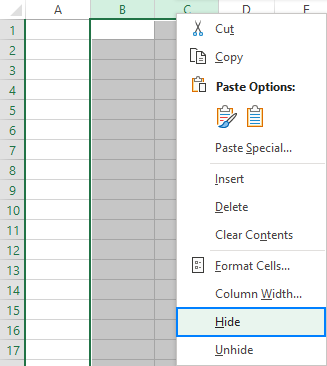
+Yes, you can hide columns in Excel without using VBA by selecting the column headers and pressing `Ctrl + 0` (zero) or right-clicking and selecting `Hide`.
How do I unhide columns in Excel using VBA?
+To unhide columns in Excel using VBA, set the `Hidden` property to `False`. For example: `Columns("A").Hidden = False`.