Using VBA variables as ranges in Excel can greatly enhance the efficiency and flexibility of your VBA code. In this article, we will explore the different ways to use VBA variables as ranges in Excel, including declaring range variables, assigning range values, and using range variables in VBA code.
Declaring Range Variables
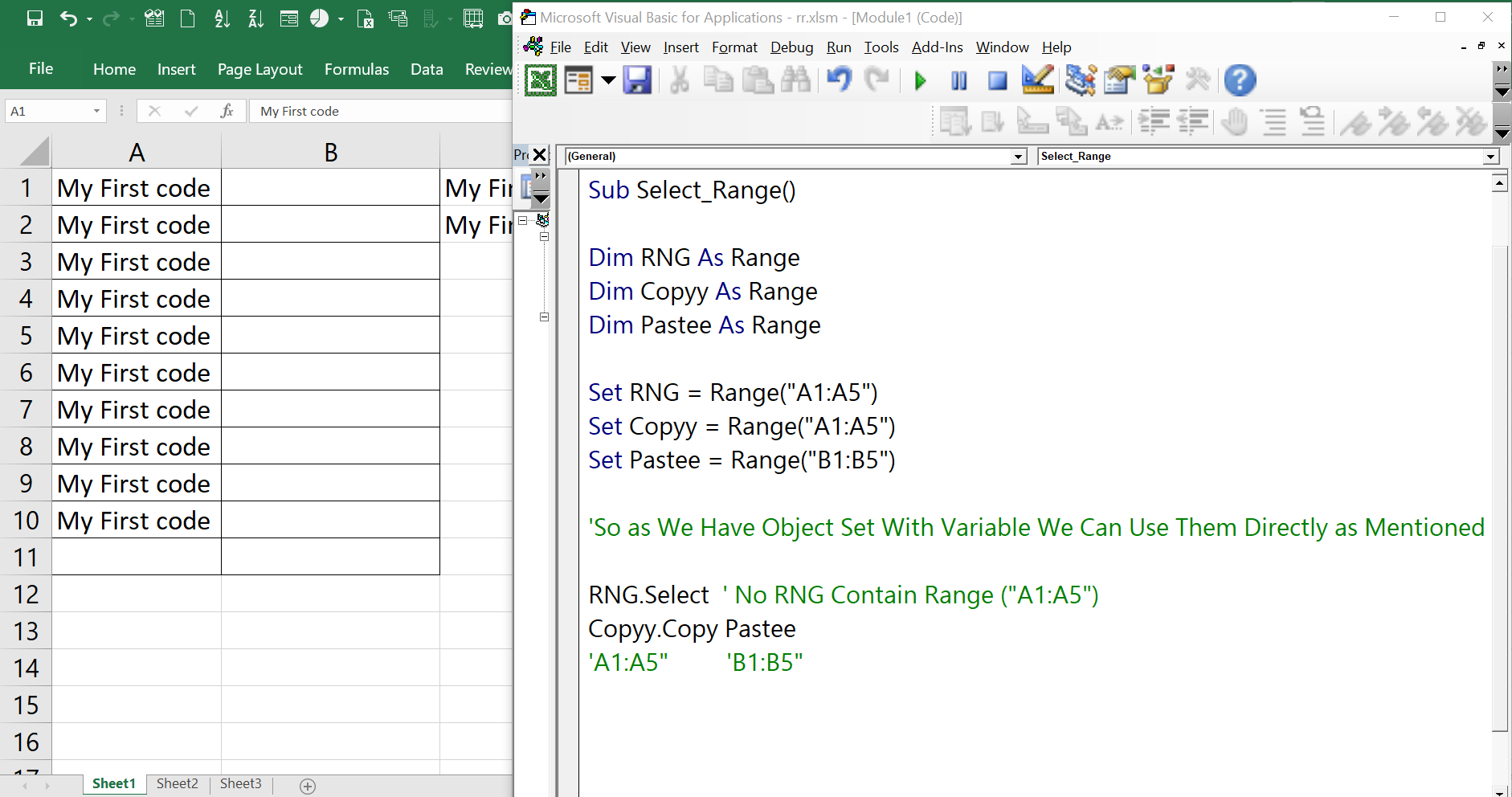
In VBA, you can declare a range variable using the Range data type. The Range data type is a built-in VBA data type that represents a range of cells in a worksheet. To declare a range variable, you use the Dim statement followed by the variable name and the As Range keywords.
Dim myRange As Range
Assigning Range Values
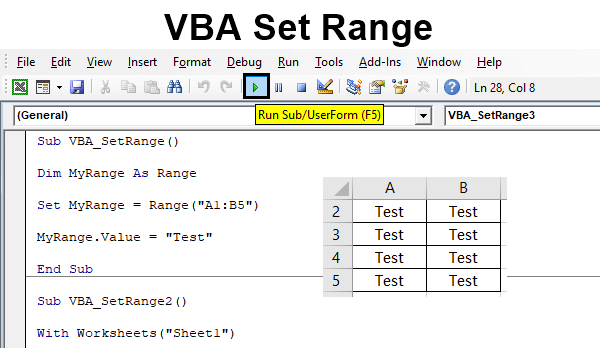
Once you have declared a range variable, you can assign a range value to it using the Set statement. The Set statement is used to assign an object reference to a variable. To assign a range value to a range variable, you use the Set statement followed by the variable name and the range value.
Set myRange = Range("A1:B2")
In this example, the myRange variable is assigned a range value that refers to the cells in the range A1:B2.
Using Range Variables in VBA Code
Range variables can be used in VBA code just like any other variable. You can use range variables to perform various operations, such as copying data, formatting cells, and inserting formulas.
Sub UseRangeVariable()
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("A1:B2")
myRange.Copy
Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
In this example, the myRange variable is used to copy the data in the range A1:B2 and paste it into the range C1:D2.
Dynamic Range Variables
One of the most powerful features of range variables is the ability to create dynamic range variables. A dynamic range variable is a range variable that can change its range value at runtime. To create a dynamic range variable, you can use the Range function with a variable argument.
Sub DynamicRangeVariable()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim startRow As Long
Dim endRow As Long
startRow = 1
endRow = 10
Set myRange = Range(Cells(startRow, 1), Cells(endRow, 2))
myRange.Copy
Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
In this example, the myRange variable is created dynamically using the Range function with variable arguments. The range value of the myRange variable changes depending on the values of the startRow and endRow variables.

Benefits of Using Range Variables
Using range variables in VBA code can have several benefits, including:
- Improved code readability: Range variables can make your code more readable by allowing you to use descriptive variable names instead of hard-coded range values.
- Increased flexibility: Range variables can be used to create dynamic range values that can change at runtime, making your code more flexible and adaptable.
- Reduced errors: Range variables can reduce errors by allowing you to use a single variable to refer to a range of cells, rather than hard-coding multiple range values.
Common Errors When Using Range Variables
When using range variables, there are several common errors to watch out for, including:
- Not setting the range variable: Range variables must be set using the
Setstatement before they can be used. - Using the wrong range value: Make sure to use the correct range value when setting the range variable.
- Not qualifying the range variable: Range variables must be qualified with the worksheet object to avoid errors.
Best Practices for Using Range Variables
To get the most out of range variables, follow these best practices:
- Use descriptive variable names: Use descriptive variable names to make your code more readable.
- Set range variables explicitly: Always set range variables explicitly using the
Setstatement. - Qualify range variables: Qualify range variables with the worksheet object to avoid errors.
Using Range Variables with Other VBA Objects
Range variables can be used with other VBA objects, such as worksheets, workbooks, and charts. To use a range variable with another VBA object, you can use the object's properties and methods to manipulate the range variable.
Using Range Variables with Worksheets
Range variables can be used with worksheets to perform various operations, such as copying data and formatting cells.
Sub UseRangeVariableWithWorksheet()
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = ActiveSheet.Range("A1:B2")
myRange.Copy
ActiveSheet.Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
In this example, the myRange variable is used with the ActiveSheet object to copy data from one range to another.
Using Range Variables with Workbooks
Range variables can be used with workbooks to perform various operations, such as opening and closing workbooks.
Sub UseRangeVariableWithWorkbook()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim myWorkbook As Workbook
Set myWorkbook = Workbooks.Open("C:\Example.xlsx")
Set myRange = myWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range("A1:B2")
myRange.Copy
myWorkbook.Sheets(2).Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
Application.CutCopyMode = False
myWorkbook.Close
End Sub
In this example, the myRange variable is used with the Workbooks object to open a workbook and copy data between worksheets.

Conclusion
Using VBA variables as ranges in Excel can greatly enhance the efficiency and flexibility of your VBA code. By declaring range variables, assigning range values, and using range variables in VBA code, you can create more readable, flexible, and error-free code. Additionally, range variables can be used with other VBA objects, such as worksheets and workbooks, to perform various operations.
By following the best practices outlined in this article, you can get the most out of range variables and take your VBA coding skills to the next level.




What is a range variable in VBA?
+A range variable in VBA is a variable that represents a range of cells in a worksheet.
How do I declare a range variable in VBA?
+To declare a range variable in VBA, use the `Dim` statement followed by the variable name and the `As Range` keywords.
How do I assign a range value to a range variable in VBA?
+To assign a range value to a range variable in VBA, use the `Set` statement followed by the variable name and the range value.