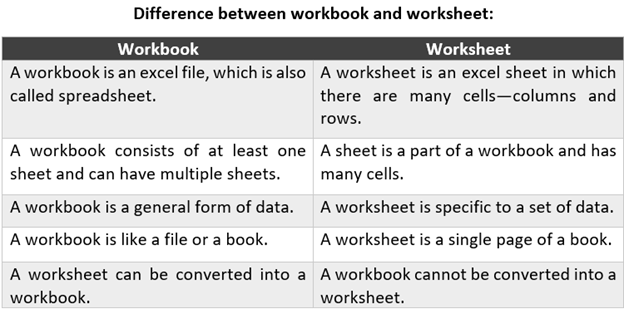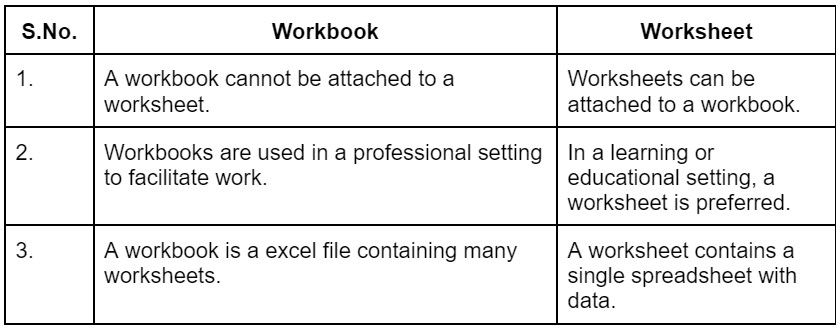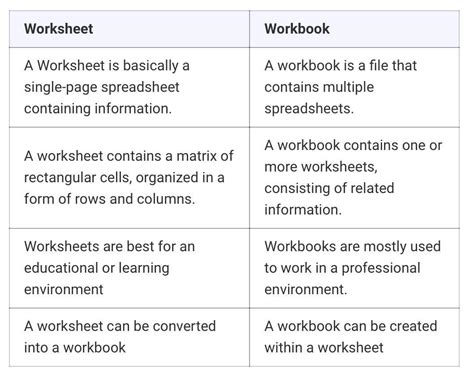
The terms "workbook" and "worksheet" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and purposes. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between a workbook and a worksheet.
When it comes to education, learning, and professional development, both workbooks and worksheets play crucial roles. They help individuals develop new skills, practice what they have learned, and track their progress. However, these two tools serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
Understanding the differences between a workbook and a worksheet is essential for teachers, educators, and learners alike. By recognizing these differences, you can choose the right tool for your specific needs and achieve your goals more effectively.
Let's dive into the 5 key differences between a workbook and a worksheet.
Difference 1: Purpose
A workbook is a comprehensive resource that provides a structured learning experience. It is designed to guide learners through a series of lessons, exercises, and activities that help them develop new skills or knowledge. Workbooks typically cover a broad range of topics and are often used in educational settings or professional training programs.
On the other hand, a worksheet is a single, self-contained document that focuses on a specific task or activity. Its primary purpose is to provide learners with a way to practice what they have learned, reinforce their understanding, or assess their knowledge. Worksheets are often used to supplement a workbook or as a standalone resource.
Difference 2: Scope
A workbook typically covers a broad range of topics and is designed to provide learners with a comprehensive understanding of a subject. It may include multiple lessons, exercises, and activities that are designed to help learners develop new skills or knowledge.
In contrast, a worksheet is a more focused resource that targets a specific skill or knowledge area. It may include a single exercise, activity, or assessment that is designed to help learners practice what they have learned.
For example, a workbook on mathematics might cover topics such as algebra, geometry, and calculus, while a worksheet on mathematics might focus on a specific topic, such as solving linear equations.
Difference 3: Structure
A workbook typically has a structured format that includes multiple sections, chapters, or lessons. Each section may include a combination of text, images, and exercises that are designed to help learners develop new skills or knowledge.
A worksheet, on the other hand, is a single document that may include a variety of formats, such as multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, or open-ended exercises. The structure of a worksheet is often more flexible than a workbook and may be tailored to meet the specific needs of learners.
For example, a workbook on language learning might include a series of lessons on grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, while a worksheet on language learning might include a single exercise that focuses on practicing verb conjugation.
Difference 4: Length
A workbook is typically a longer document that may range from several dozen to several hundred pages. It is designed to provide learners with a comprehensive resource that they can use over an extended period.
A worksheet, on the other hand, is a shorter document that may range from a single page to several pages. It is designed to provide learners with a focused resource that they can use to practice what they have learned or assess their knowledge.
For example, a workbook on project management might include 200 pages of text, images, and exercises, while a worksheet on project management might include a single page with a series of multiple-choice questions.
Difference 5: Assessment
A workbook often includes assessments or evaluations that are designed to help learners track their progress or measure their understanding. These assessments may include quizzes, tests, or exams that are designed to evaluate learners' knowledge or skills.
A worksheet, on the other hand, may include assessments or evaluations, but they are often less formal than those found in a workbook. Worksheets may include self-assessment checks or peer review exercises that are designed to help learners evaluate their own understanding or provide feedback to their peers.
For example, a workbook on leadership development might include a final exam that evaluates learners' understanding of key concepts, while a worksheet on leadership development might include a self-assessment check that helps learners evaluate their own leadership skills.
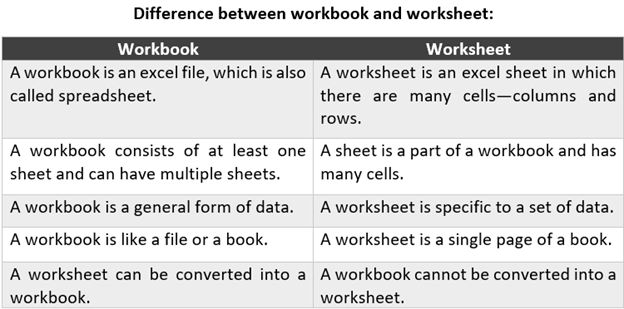
In conclusion, while both workbooks and worksheets are essential tools for learning and professional development, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. By understanding the 5 key differences between a workbook and a worksheet, you can choose the right tool for your specific needs and achieve your goals more effectively.
Whether you are a teacher, educator, or learner, recognizing the differences between a workbook and a worksheet can help you create more effective learning experiences, improve learner engagement, and achieve better outcomes.
Gallery of Workbook and Worksheet Examples




FAQs
What is the main difference between a workbook and a worksheet?
+The main difference between a workbook and a worksheet is their purpose. A workbook is a comprehensive resource that provides a structured learning experience, while a worksheet is a single, self-contained document that focuses on a specific task or activity.
Can a workbook be used as a worksheet?
+No, a workbook cannot be used as a worksheet. A workbook is a longer document that provides a comprehensive learning experience, while a worksheet is a shorter document that focuses on a specific task or activity.
How can I use a workbook and a worksheet together?
+You can use a workbook and a worksheet together by using the workbook as a comprehensive resource and the worksheet as a supplement to practice what you have learned. This can help you reinforce your understanding and improve your skills.