File management is an essential aspect of working with VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), particularly when automating tasks or creating tools that interact with the file system. Renaming files is one of the fundamental file management operations that can be efficiently handled using VBA. This article will explore five different methods to change a file name in VBA, highlighting their syntax, usage, and applicability in various scenarios.
Understanding the Basics of File Renaming in VBA
Before diving into the methods, it's crucial to understand the basic concepts involved in renaming files using VBA. The primary object that interacts with files and folders is the FileSystemObject (FSO), which is part of the Microsoft Scripting Runtime library. By using the FSO, you can easily manipulate files and folders.
To work with the FSO, you first need to set a reference to the Microsoft Scripting Runtime library in your VBA project. Here's how:
- Open the VBA editor (Press
Alt+F11or navigate to Developer Tab and click Visual Basic). - Go to Tools > References.
- Check the box next to "Microsoft Scripting Runtime" and click OK.
Method 1: Using the Name Statement
The simplest method to rename a file in VBA is by using the Name statement. This method is straightforward and does not require the use of the FSO.
Sub RenameFileUsingNameStatement()
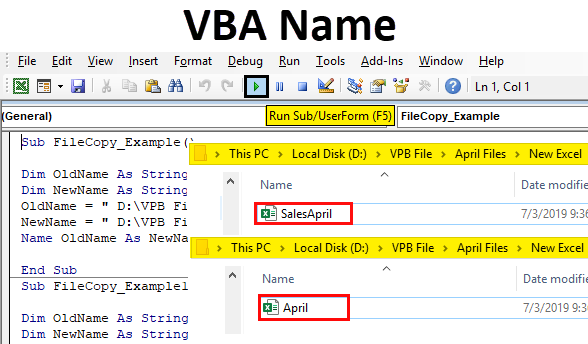
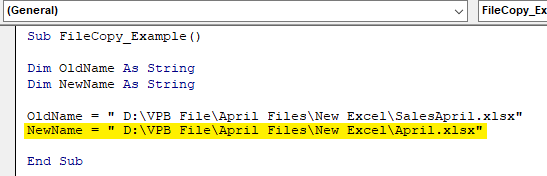
Name "C:\Source\OldFileName.txt" As "C:\Destination\NewFileName.txt"
End Sub
This method directly renames the file from OldFileName.txt to NewFileName.txt, moving it from the Source to the Destination folder if the paths differ.
Method 2: Using the MoveFile Method of the FileSystemObject
When using the FSO, you can rename a file by moving it to the same location with a different name. This is achieved with the MoveFile method.
Sub RenameFileUsingMoveFileMethod()
Dim fso As FileSystemObject
Set fso = New FileSystemObject
fso.MoveFile "C:\Source\OldFileName.txt", "C:\Source\NewFileName.txt"
Set fso = Nothing
End Sub
In this example, the file OldFileName.txt is renamed to NewFileName.txt within the same folder.
Method 3: Using the MoveFile Method with a Different Path
The MoveFile method is also capable of moving a file to a different location and renaming it simultaneously.
Sub RenameFileAndMoveToDifferentPath()
Dim fso As FileSystemObject
Set fso = New FileSystemObject
fso.MoveFile "C:\Source\OldFileName.txt", "C:\Destination\NewFileName.txt"
Set fso = Nothing
End Sub
Here, not only is the file renamed, but it's also moved from the Source folder to the Destination folder.
Method 4: Using the GetFile Method with the Name Property
This method involves getting a reference to the file object using the GetFile method and then changing its Name property.
Sub RenameFileUsingGetFileMethod()
Dim fso As FileSystemObject
Dim file As File
Set fso = New FileSystemObject
Set file = fso.GetFile("C:\Source\OldFileName.txt")
file.Name = "NewFileName.txt"
Set file = Nothing
Set fso = Nothing
End Sub
This method directly changes the name of the file to NewFileName.txt without moving it.
Method 5: Renaming Multiple Files
Sometimes, you might need to rename multiple files based on certain criteria. This can be achieved by looping through the files in a folder and applying the rename operation.
Sub RenameMultipleFiles()
Dim fso As FileSystemObject
Dim folder As Folder
Dim file As File
Dim i As Integer
Set fso = New FileSystemObject
Set folder = fso.GetFolder("C:\Source")
i = 1
For Each file In folder.Files
If Right(file.Name, 4) = ".txt" Then
file.Name = "NewFileName_" & i & ".txt"
i = i + 1
End If
Next file
Set file = Nothing
Set folder = Nothing
Set fso = Nothing
End Sub
In this example, all .txt files in the Source folder are renamed with a prefix NewFileName_ followed by a number.
Conclusion
Renaming files in VBA can be accomplished through various methods, each with its specific use cases. By understanding the different approaches and their capabilities, you can efficiently manage files and automate tasks in your VBA projects.

Gallery of VBA File Renaming Techniques




What is the most efficient way to rename a file in VBA?
+The most efficient way to rename a file in VBA depends on the specific requirements of your task. If you're renaming a single file, using the `Name` statement or the `MoveFile` method of the `FileSystemObject` can be efficient. For more complex operations, such as renaming multiple files based on certain criteria, looping through files and applying the rename operation might be necessary.
How do I reference the Microsoft Scripting Runtime library in my VBA project?
+To reference the Microsoft Scripting Runtime library, open the VBA editor, go to Tools > References, and check the box next to "Microsoft Scripting Runtime". This allows you to use the `FileSystemObject` and other classes and methods provided by this library.
What is the purpose of the `FileSystemObject` in VBA?
+The `FileSystemObject` is a key component in VBA for interacting with the file system. It allows you to perform various file and folder operations, such as creating, deleting, moving, and renaming files and folders, making it a powerful tool for file management tasks.