Working with ranges in VBA can be a powerful way to manipulate and analyze data in Excel. One common task is calculating the sum of a range, which can be accomplished in a few different ways. Here, we'll explore the easiest methods to sum a range in VBA, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced users.
Understanding Ranges in VBA
Before diving into calculating sums, it's essential to understand how to refer to ranges in VBA. A range can be any cell or group of cells in a worksheet. You can refer to a range using its address (e.g., Range("A1")) or by using the Cells property to specify the row and column (e.g., Cells(1, 1)).
Method 1: Using the Range Object
One of the most straightforward ways to sum a range is by using the Sum method directly on a Range object.
Sub SumRangeExample1()
Dim sumOfRange As Double
sumOfRange = Application.Sum(Range("A1:A10"))
MsgBox "The sum of the range A1:A10 is " & sumOfRange
End Sub
In this example, Application.Sum calculates the sum of the values in the range A1:A10. Note that this method ignores non-numeric values.
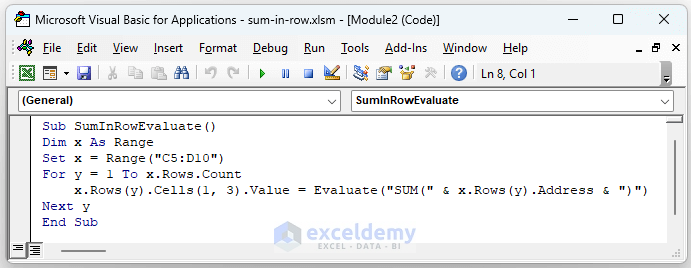
Method 2: Using Evaluate
Another way to sum a range is by using the Evaluate method, which evaluates a string as if it were a formula.
Sub SumRangeExample2()
Dim sumOfRange As Double
sumOfRange = Evaluate("SUM(A1:A10)")
MsgBox "The sum of the range A1:A10 is " & sumOfRange
End Sub
This method is particularly useful when you need to construct the range dynamically or for more complex calculations.
Method 3: Looping Through a Range
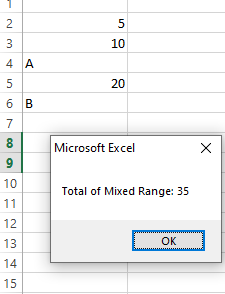
While not always the most efficient for large datasets, looping through each cell in a range can be a straightforward approach for smaller ranges or when you need to perform additional checks on each cell.
Sub SumRangeExample3()
Dim cell As Range
Dim sumOfRange As Double
For Each cell In Range("A1:A10")
If IsNumeric(cell.Value) Then
sumOfRange = sumOfRange + cell.Value
End If
Next cell
MsgBox "The sum of the range A1:A10 is " & sumOfRange
End Sub
This method provides more control over how non-numeric values are handled.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method
Each method has its advantages. Application.Sum and Evaluate are generally faster and more efficient for calculating sums directly. Looping through a range provides more flexibility but can be slower for large ranges. Choose the method that best fits your specific needs and data.
To further enhance your VBA skills, consider exploring more advanced topics such as working with arrays, using Excel's built-in functions in VBA, and optimizing code for performance.

Gallery of VBA Sum Range Examples




FAQs
How do I sum a range in VBA efficiently?
+Use the `Application.Sum` method for efficiency. It's specifically designed for summing ranges and ignores non-numeric values.
Can I dynamically sum a range based on user input?
+Why might I choose to loop through a range instead of using a built-in method?
+Looping through a range provides more control over the summing process, allowing you to handle non-numeric values differently or perform additional operations on each cell.