Copying ranges in Excel VBA can be a daunting task for beginners, but with the right guidance, it can be made easy. In this article, we will delve into the world of Excel VBA and explore the various ways to copy ranges with ease.
Understanding Ranges in Excel VBA
Before we dive into the copying process, it's essential to understand what ranges are in Excel VBA. A range refers to a group of cells that can be referenced by a single name or identifier. Ranges can be a single cell, a row, a column, or a group of cells.
Why Copy Ranges in Excel VBA?
Copying ranges in Excel VBA is a common task that can be useful in various scenarios. For instance, you might want to copy data from one worksheet to another, or from one workbook to another. You might also want to copy formulas or formatting from one range to another.
Basic Syntax for Copying Ranges
The basic syntax for copying ranges in Excel VBA is as follows:
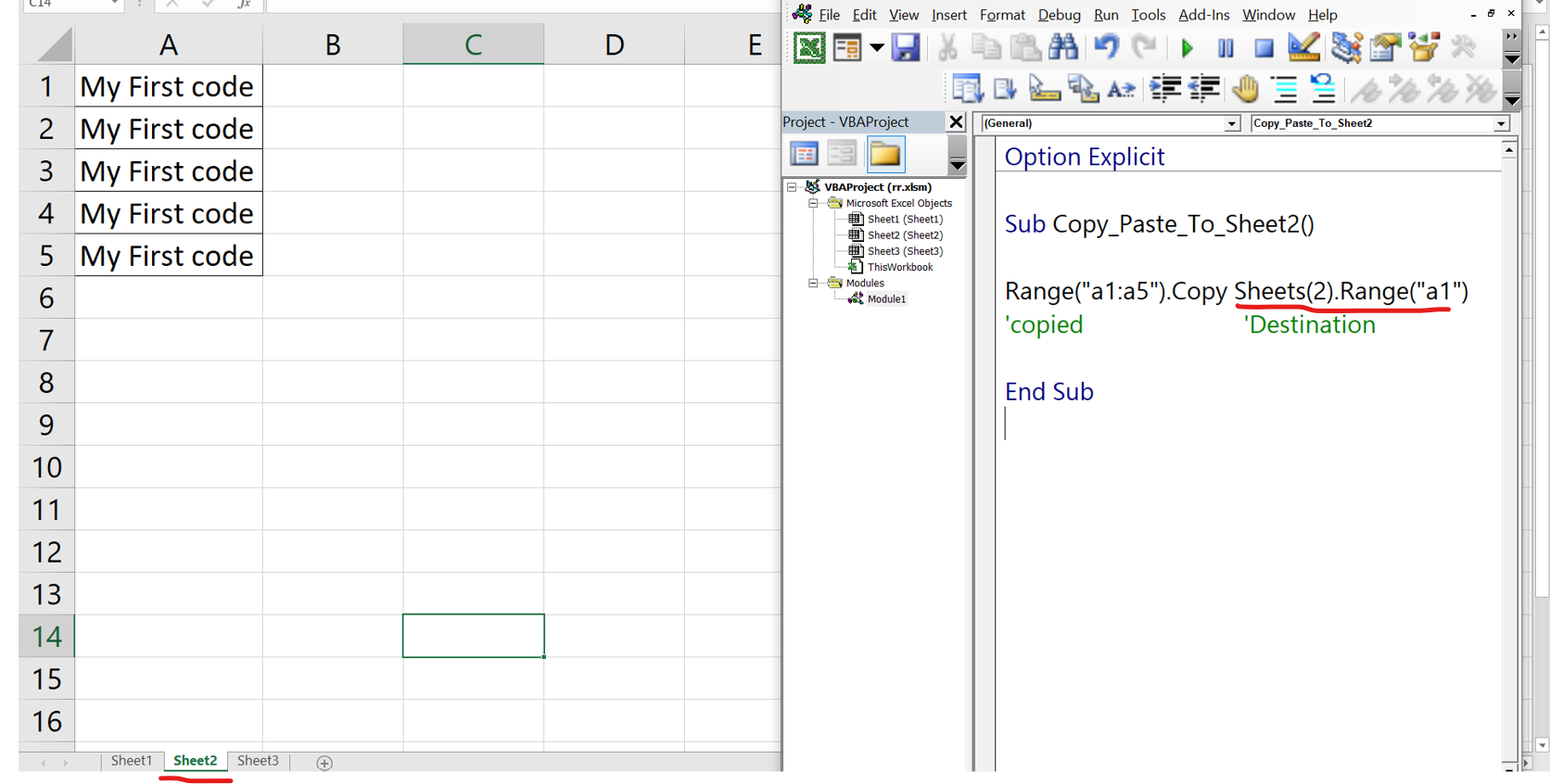
Range("SourceRange").Copy Destination:=Range("DestinationRange")
In this syntax:
Range("SourceRange")refers to the range that you want to copy.Copyis the method that copies the range.Destination:=Range("DestinationRange")specifies the destination range where the data will be copied.
Examples of Copying Ranges
Here are some examples of copying ranges in Excel VBA:
Example 1: Copying a Single Cell
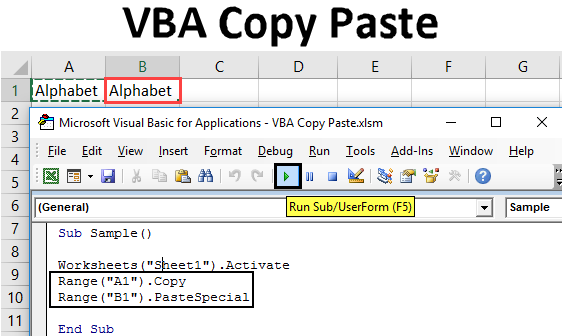
Range("A1").Copy Destination:=Range("B1")
In this example, the value in cell A1 is copied to cell B1.
Example 2: Copying a Range of Cells
Range("A1:B2").Copy Destination:=Range("C1:D2")
In this example, the values in the range A1:B2 are copied to the range C1:D2.
Example 3: Copying a Row
Range("A1").EntireRow.Copy Destination:=Range("B1").EntireRow
In this example, the entire row containing cell A1 is copied to the entire row containing cell B1.
Example 4: Copying a Column
Range("A1").EntireColumn.Copy Destination:=Range("B1").EntireColumn
In this example, the entire column containing cell A1 is copied to the entire column containing cell B1.
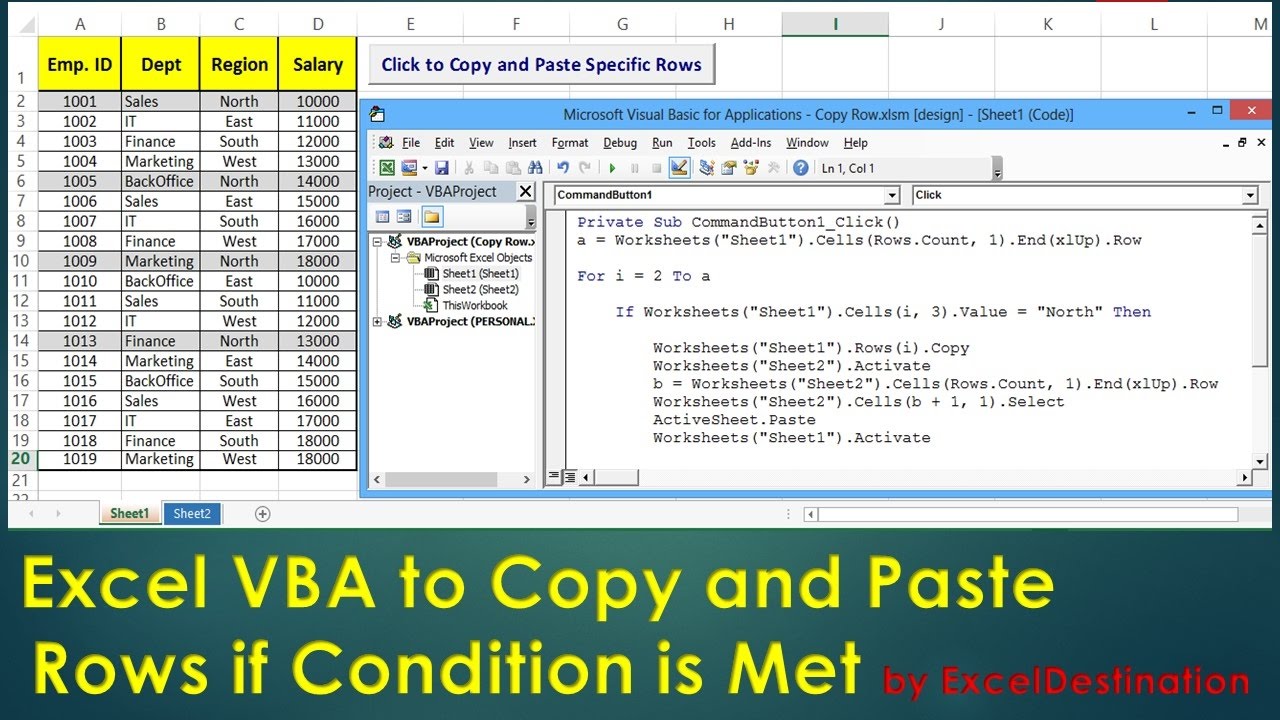
Advanced Copying Techniques
In addition to the basic syntax, there are several advanced techniques that you can use to copy ranges in Excel VBA. These include:
- Copying Formatting: You can copy formatting from one range to another using the
PasteSpecialmethod.
Range("A1:B2").Copy
Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial xlPasteFormats
Application.CutCopyMode = False
- Copying Formulas: You can copy formulas from one range to another using the
PasteSpecialmethod.
Range("A1:B2").Copy
Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial xlPasteFormulas
Application.CutCopyMode = False
- Copying Values and Formatting: You can copy values and formatting from one range to another using the
PasteSpecialmethod.
Range("A1:B2").Copy
Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial xlPasteValuesAndNumberFormats
Application.CutCopyMode = False
Tips and Tricks
Here are some tips and tricks to keep in mind when copying ranges in Excel VBA:
- Use the
Application.CutCopyMode = Falsestatement to clear the clipboard after copying. - Use the
Range.Copymethod instead of theWorksheet.Copymethod to copy ranges. - Use the
Destinationargument to specify the destination range. - Use the
PasteSpecialmethod to copy formatting, formulas, or values.
Gallery of Copying Ranges




FAQs
What is the basic syntax for copying ranges in Excel VBA?
+The basic syntax for copying ranges in Excel VBA is `Range("SourceRange").Copy Destination:=Range("DestinationRange")`.
How do I copy formatting from one range to another?
+You can copy formatting from one range to another using the `PasteSpecial` method. For example: `Range("A1:B2").Copy` `Range("C1:D2").PasteSpecial xlPasteFormats` `Application.CutCopyMode = False`.
What is the difference between `Range.Copy` and `Worksheet.Copy`?
+`Range.Copy` copies the range, while `Worksheet.Copy` copies the entire worksheet.
By following the examples and tips outlined in this article, you should be able to copy ranges in Excel VBA with ease. Remember to use the Range.Copy method, specify the destination range, and clear the clipboard after copying. Happy coding!