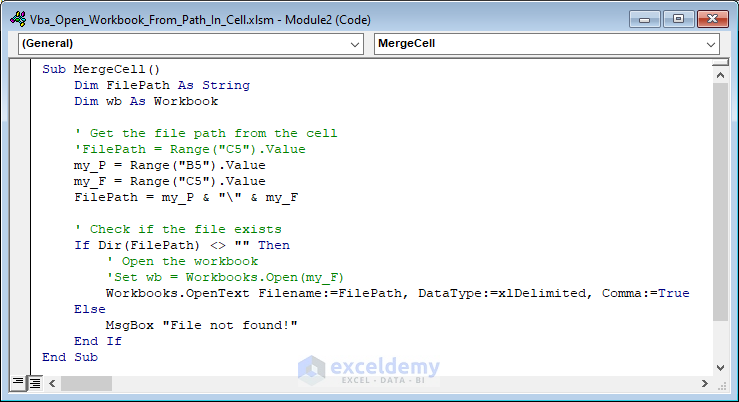
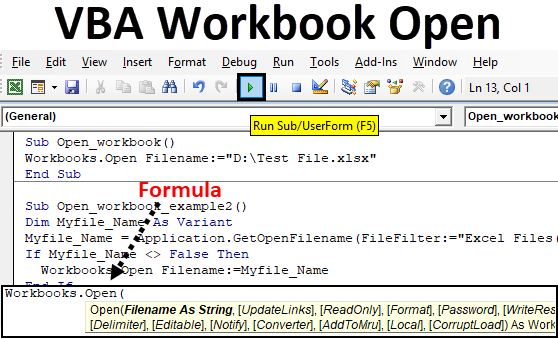
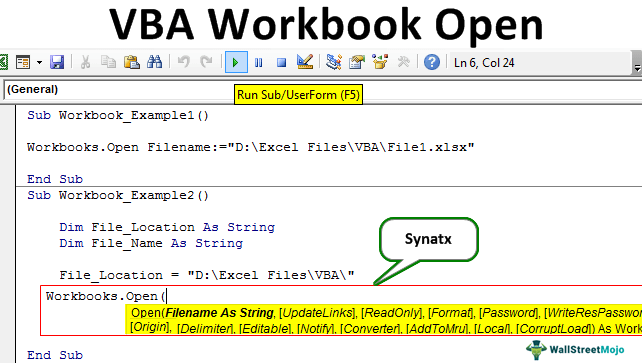
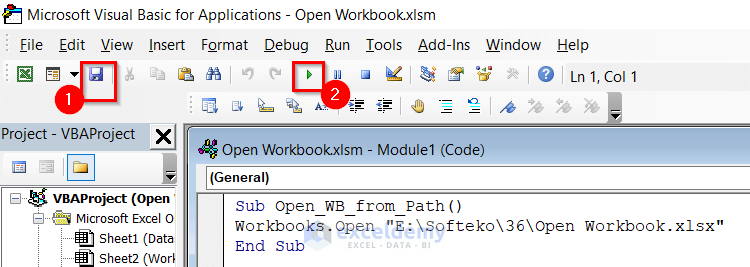
Opening a workbook in VBA is a fundamental skill for any Excel automation task. Whether you're trying to import data, update existing workbooks, or create new ones, being able to open workbooks programmatically is essential. In this article, we'll explore five different ways to open a workbook in VBA.
Excel VBA is a powerful tool for automating tasks in Excel, but it requires a good understanding of its syntax and functionality. By mastering the different methods of opening workbooks, you'll be able to tackle a wide range of automation tasks with confidence.
Why is it Important to Open Workbooks in VBA?
Before we dive into the different methods of opening workbooks, let's quickly explore why this skill is so important. Opening workbooks in VBA allows you to:
- Import data from external sources
- Update existing workbooks with new data or formatting
- Create new workbooks based on templates or existing files
- Automate tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming or prone to errors
By opening workbooks programmatically, you can streamline your workflow, reduce errors, and increase productivity.
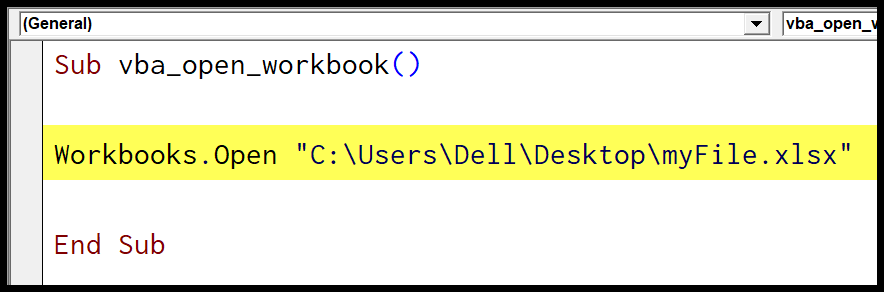
Method 1: Using the Workbooks.Open Method
The most straightforward way to open a workbook in VBA is by using the Workbooks.Open method. This method takes the file path and name of the workbook as an argument and returns a Workbook object that you can use to manipulate the workbook.
Here's an example of how to use the Workbooks.Open method:
Sub OpenWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:\Path\To\Workbook.xlsx")
' Now you can use the wb object to manipulate the workbook
End Sub
Method 2: Using the Application.Workbooks.Open Method
Another way to open a workbook is by using the Application.Workbooks.Open method. This method is similar to the Workbooks.Open method, but it uses the Application object to access the Workbooks collection.
Here's an example of how to use the Application.Workbooks.Open method:
Sub OpenWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Application.Workbooks.Open("C:\Path\To\Workbook.xlsx")
' Now you can use the wb object to manipulate the workbook
End Sub
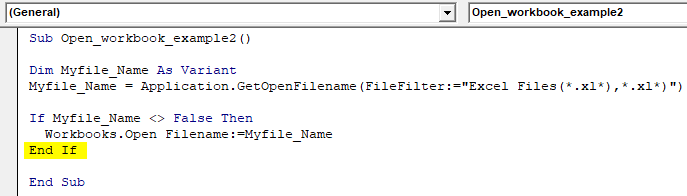
Method 3: Using the FileDialog Object
If you need to open a workbook based on user input, you can use the FileDialog object to prompt the user to select a file. This method is useful when you don't know the file path or name in advance.
Here's an example of how to use the FileDialog object:
Sub OpenWorkbook()
Dim fd As FileDialog
Set fd = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker)
fd.AllowMultiSelect = False
fd.Show
If fd.SelectedItems.Count > 0 Then
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(fd.SelectedItems(1))
' Now you can use the wb object to manipulate the workbook
End If
End Sub
Method 4: Using the Environ Function
If you need to open a workbook based on an environment variable, you can use the Environ function to retrieve the file path. This method is useful when you need to open a workbook based on a system-wide setting.
Here's an example of how to use the Environ function:
Sub OpenWorkbook()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = Environ$("USERPROFILE") & "\Documents\Workbook.xlsx"
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(filePath)
' Now you can use the wb object to manipulate the workbook
End Sub
Method 5: Using the Shell Function
Finally, you can use the Shell function to open a workbook by executing a shell command. This method is useful when you need to open a workbook from a external application or script.
Here's an example of how to use the Shell function:
Sub OpenWorkbook()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = "C:\Path\To\Workbook.xlsx"
Shell "excel """ & filePath & """", vbNormalFocus
' Now you can use the workbook object to manipulate the workbook
End Sub

Gallery of VBA Open Workbook




Frequently Asked Questions
How do I open a workbook in VBA?
+There are several ways to open a workbook in VBA, including using the `Workbooks.Open` method, `Application.Workbooks.Open` method, `FileDialog` object, `Environ` function, and `Shell` function.
What is the difference between `Workbooks.Open` and `Application.Workbooks.Open`?
+Both methods can be used to open a workbook, but `Application.Workbooks.Open` uses the `Application` object to access the `Workbooks` collection, while `Workbooks.Open` uses the `Workbooks` collection directly.
How do I open a workbook based on user input?
+You can use the `FileDialog` object to prompt the user to select a file, and then open the workbook based on the selected file path.
We hope this article has helped you learn the different ways to open a workbook in VBA. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, mastering these skills will help you automate tasks and increase productivity in Excel.