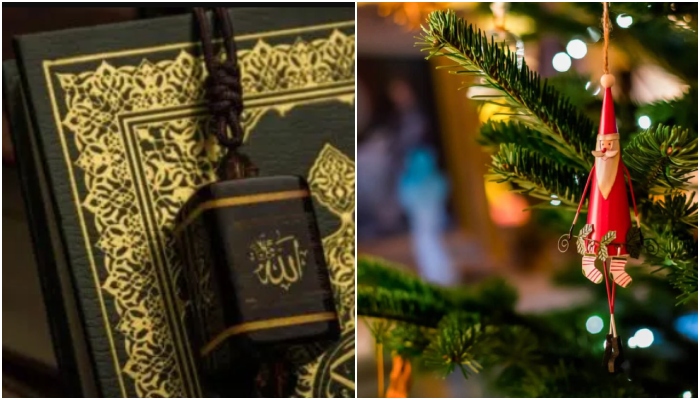
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, it's essential to understand and appreciate the diverse traditions and holidays that make up the fabric of our global community. Two significant events that occur around the same time of the year are the Muslim holidays of Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, and the Christian celebration of Christmas. In this article, we'll delve into the differences and similarities between these holidays, exploring their history, significance, and cultural practices.
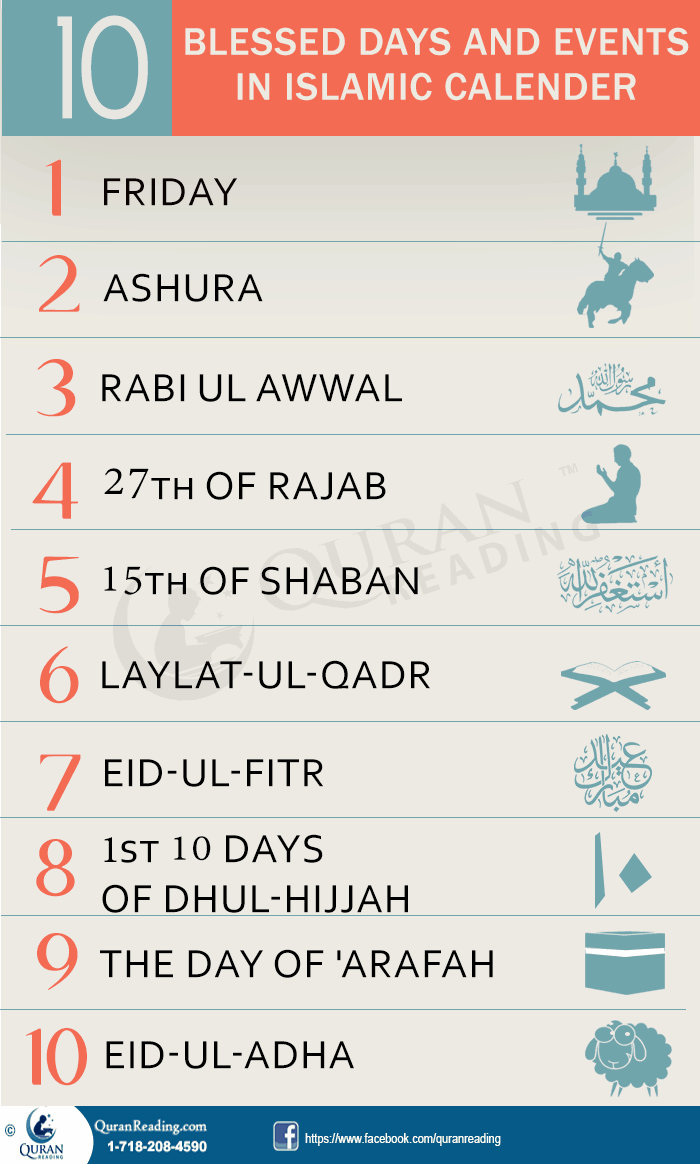
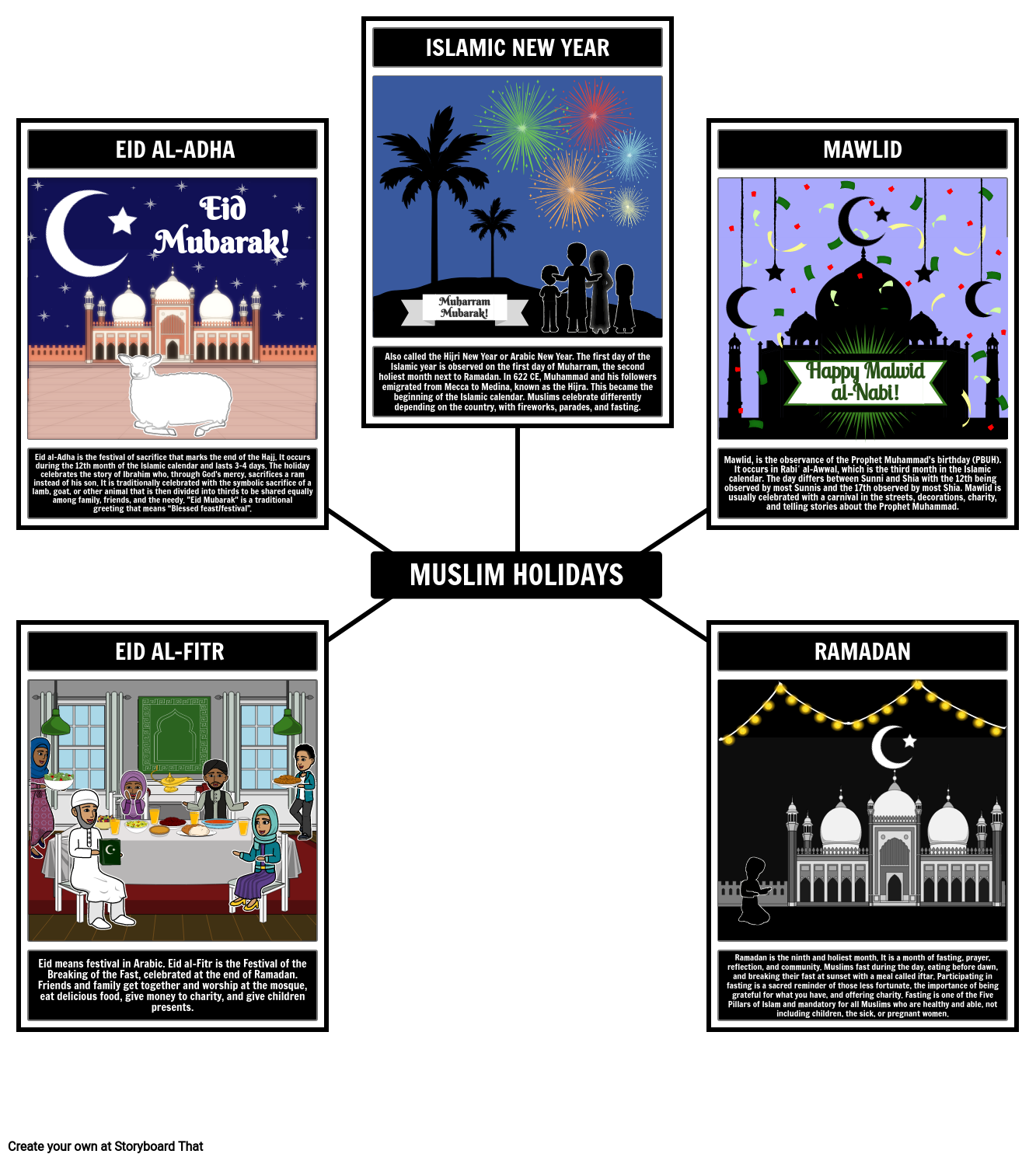
Eid al-Fitr, also known as the "Festival of Breaking the Fast," marks the end of Ramadan, the Islamic holy month of fasting. This joyous occasion is a time for Muslims to come together with family and friends, exchange gifts, and indulge in traditional foods. Eid al-Adha, on the other hand, commemorates the willingness of the Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son as an act of obedience to God. This holiday is also a celebration of the end of the Hajj pilgrimage, a sacred journey to the holy city of Mecca.
Christmas, as we all know, is a holiday commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ and is observed by Christians around the world. The festive season is often associated with decorations, gift-giving, and quality time with loved ones. While these holidays may seem vastly different on the surface, they share some common themes and values.

Understanding the Significance of Muslim Holidays
To truly appreciate the differences and similarities between Muslim holidays and Christmas, it's crucial to understand the significance of these events in the Islamic calendar. Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are two of the most important holidays in Islam, and they hold a special place in the hearts of Muslims worldwide.
Eid al-Fitr is a celebration of the end of Ramadan, a month of fasting, reflection, and spiritual growth. During this time, Muslims abstain from food and drink from dawn to sunset, seeking to develop self-control, empathy, and a deeper connection with their faith. The act of fasting is a means of purifying the soul, and the end of Ramadan is a time for rejuvenation and renewal.
Eid al-Adha, on the other hand, is a celebration of sacrifice, obedience, and devotion. The story of Prophet Ibrahim and his son Ismail (Ishmael) serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of faith and trust in God's will. This holiday is also a time for Muslims to reflect on their own lives, re-evaluating their priorities and striving to become better versions of themselves.
The Cultural Significance of Muslim Holidays
Muslim holidays are deeply rooted in cultural and traditional practices, which vary across different regions and communities. Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are often marked with festive foods, decorations, and gift-giving. In many Muslim-majority countries, these holidays are public holidays, and people come together to celebrate with family and friends.
One of the most iconic traditions associated with Eid al-Fitr is the exchange of gifts, particularly for children. This practice is rooted in the Islamic tradition of giving charity and spreading joy during times of celebration. In many Muslim households, traditional foods such as dates, samosas, and kebabs are prepared and shared with loved ones.

Unwrapping the Magic of Christmas Traditions
Christmas, as we all know, is a time for celebration, gift-giving, and merriment. This festive holiday has a rich history, dating back to the 4th century when it was first observed as a Christian holiday. Over time, Christmas has evolved into a global phenomenon, incorporating diverse cultural and traditional practices.
At its core, Christmas is a celebration of the birth of Jesus Christ, and many Christians around the world mark this occasion with special church services, prayers, and hymns. The festive season is also a time for family gatherings, feasting, and exchanging gifts.
One of the most iconic Christmas traditions is the decorating of trees, a practice that originated in 16th-century Germany. Today, Christmas trees are a ubiquitous feature of holiday celebrations, often adorned with lights, ornaments, and tinsel.

The Cultural Significance of Christmas
Christmas is deeply ingrained in Western culture, and its traditions have been shaped by centuries of history and cultural exchange. The holiday has evolved over time, incorporating diverse practices and customs from around the world.
In many Christian-majority countries, Christmas is a public holiday, and people come together to celebrate with family and friends. The festive season is often marked with traditional foods, such as roast turkey, mince pies, and Christmas pudding.
One of the most iconic Christmas traditions is the exchange of gifts, particularly for children. This practice is rooted in the Christian tradition of giving and sharing, reflecting the values of kindness, generosity, and compassion.
Comparing Muslim Holidays and Christmas Traditions
While Muslim holidays and Christmas traditions may seem vastly different on the surface, they share some common themes and values. Both Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, as well as Christmas, are celebrations of faith, family, and community.
One of the most striking similarities between these holidays is the emphasis on charity and giving. In Islam, the practice of zakat (charity) is one of the five pillars of the faith, and Muslims are encouraged to give to those in need during times of celebration. Similarly, Christmas is a time for giving and sharing, reflecting the values of kindness and generosity.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Muslim holidays and Christmas traditions are two distinct yet connected threads in the rich tapestry of global celebrations. While these holidays may seem vastly different on the surface, they share a common humanity, reflecting the values of faith, family, and community.
By exploring the history, significance, and cultural practices associated with these holidays, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and richness of human experience. Whether you celebrate Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, or Christmas, the underlying message is the same – a message of love, compassion, and kindness.




Gallery of Muslim Holidays and Christmas Traditions
What is the significance of Eid al-Fitr?
+Eid al-Fitr is a celebration of the end of Ramadan, a month of fasting, reflection, and spiritual growth. It is a time for Muslims to come together with family and friends, exchange gifts, and indulge in traditional foods.
What is the story behind Christmas?
+Christmas is a celebration of the birth of Jesus Christ, and many Christians around the world mark this occasion with special church services, prayers, and hymns.
How do Muslims celebrate Eid al-Adha?
+Eid al-Adha is a celebration of sacrifice, obedience, and devotion. Muslims often mark this occasion with traditional foods, decorations, and gift-giving.