Calculating heat loss is an essential step in designing and optimizing heating systems, ensuring that your home or building is warm and cozy while minimizing energy consumption. Heat loss refers to the amount of heat that escapes from a building due to various factors, such as insulation, windows, and exterior walls. By understanding how to calculate heat loss, you can determine the size of the heating system required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Heat loss calculations can seem complex, but by breaking down the process into manageable steps, you can easily determine the heat loss of your home or building. In this article, we will guide you through the 5 easy steps to calculate heat loss.
The Importance of Accurate Heat Loss Calculations
Accurate heat loss calculations are crucial in ensuring that your heating system operates efficiently and effectively. If the heat loss is underestimated, the heating system may not provide enough heat, leading to a cold and uncomfortable indoor environment. On the other hand, overestimating heat loss can result in an oversized heating system, which can lead to increased energy consumption and higher energy bills.
Step 1: Determine the Building's Exterior Dimensions
To calculate heat loss, you need to determine the building's exterior dimensions, including the length, width, and height of the walls, as well as the area of the windows and doors. You can obtain this information from the building's blueprints or by taking measurements yourself.

Step 2: Identify the Insulation Levels
Next, you need to identify the insulation levels of the building's exterior walls, floor, and ceiling. Insulation levels are measured in terms of R-values, which indicate the level of thermal resistance. You can obtain this information from the building's construction plans or by consulting with a professional.
Typical Insulation Levels
- Walls: R-13 to R-19
- Floor: R-19 to R-25
- Ceiling: R-25 to R-38
Step 3: Determine the Window and Door Areas
Windows and doors are significant sources of heat loss, so it's essential to determine their areas accurately. Measure the length and width of each window and door, and calculate their total area.

Step 4: Calculate the Heat Loss
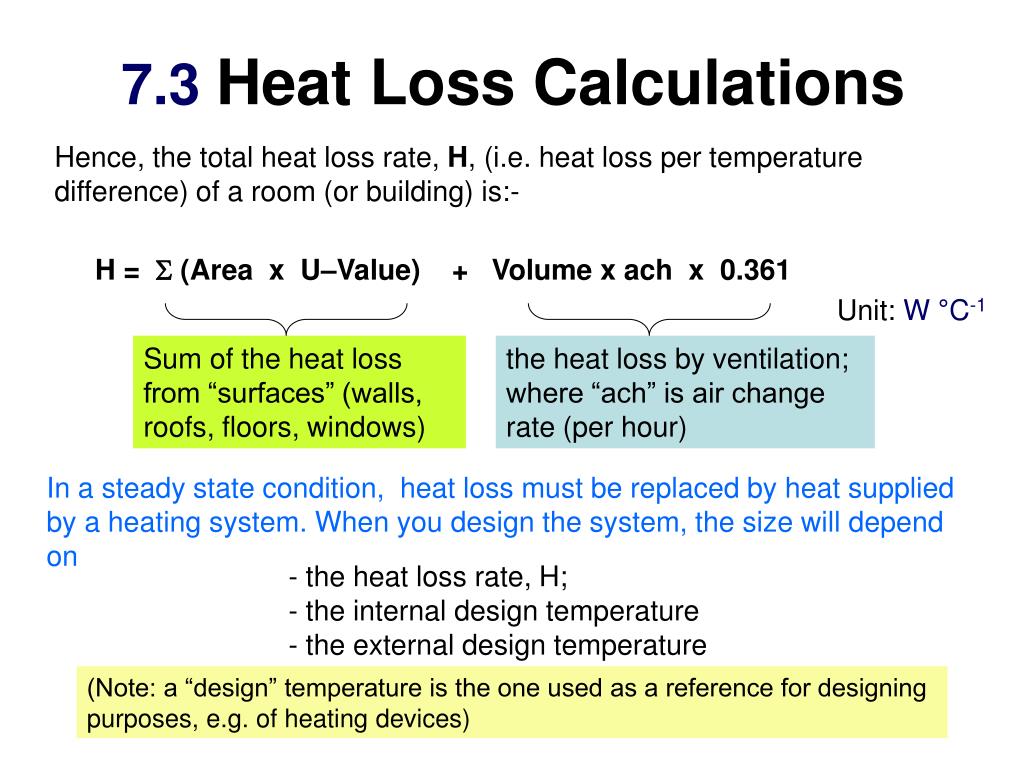
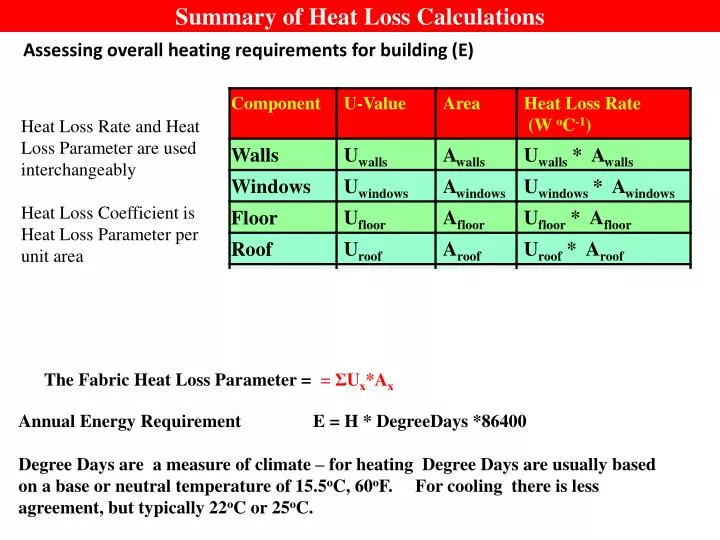
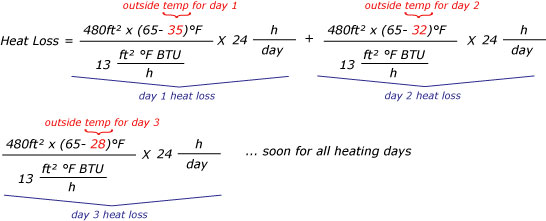
Using the data collected in the previous steps, you can calculate the heat loss using the following formula:
Heat Loss (BTU/h) = (Surface Area x U-Value x Temperature Difference)
Where:
- Surface Area: The area of the exterior walls, floor, and ceiling
- U-Value: The thermal transmittance of the building envelope (walls, floor, and ceiling)
- Temperature Difference: The difference between the indoor and outdoor temperatures
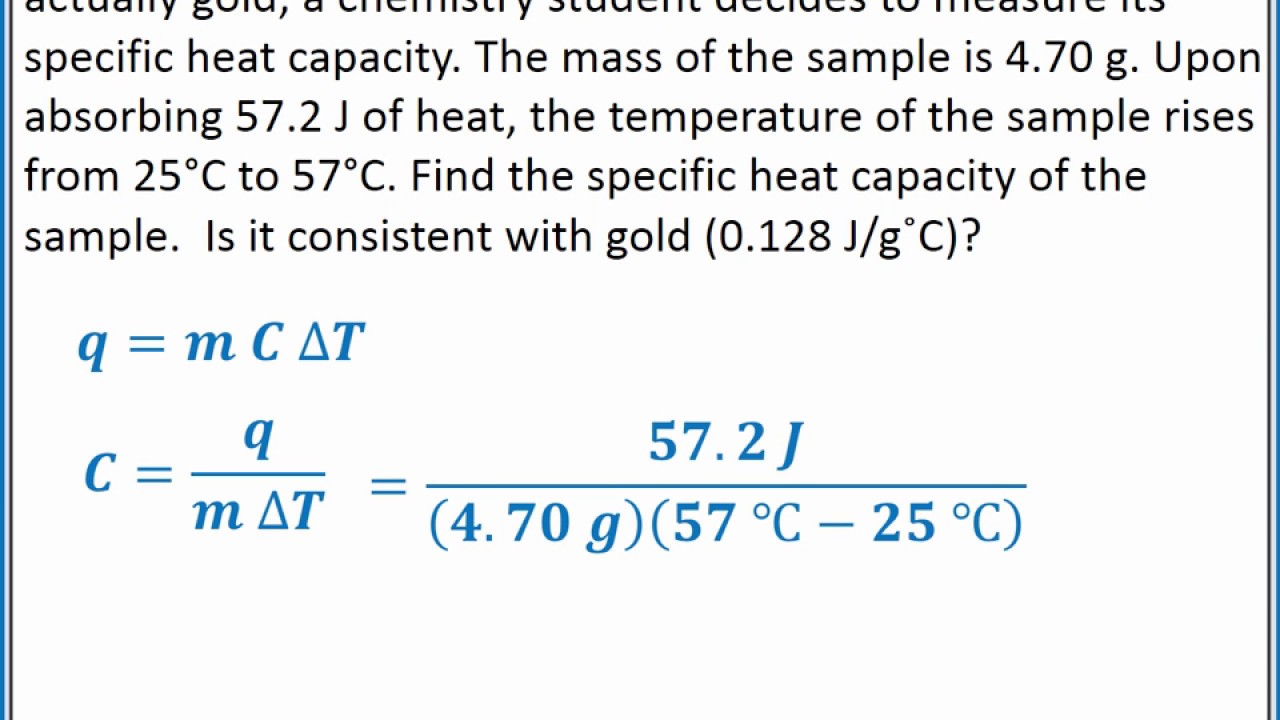
Heat Loss Calculation Example
- Surface Area: 1,000 sq. ft.
- U-Value: 0.05 (typical value for a well-insulated building)
- Temperature Difference: 70°F (indoor) - 40°F (outdoor) = 30°F
- Heat Loss: (1,000 sq. ft. x 0.05 x 30°F) = 15,000 BTU/h
Step 5: Consider Additional Factors
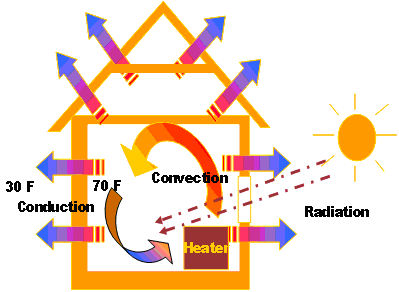
Finally, you need to consider additional factors that can affect heat loss, such as:
- Infiltration: The movement of air through cracks and gaps in the building envelope
- Radiation: The transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves
- Convection: The transfer of heat through moving air
These factors can be estimated using various calculation methods, such as the infiltration rate and radiation coefficients.

Gallery of Heat Loss Calculation Examples




FAQs
What is the purpose of heat loss calculations?
+Heat loss calculations are used to determine the amount of heat that escapes from a building, allowing for the design and optimization of heating systems.
What factors affect heat loss in a building?
+Heat loss is affected by various factors, including insulation levels, window and door areas, infiltration, radiation, and convection.
How can I reduce heat loss in my building?
+You can reduce heat loss by improving insulation, sealing gaps and cracks, installing energy-efficient windows and doors, and using radiant barriers.
By following these 5 easy steps, you can accurately calculate heat loss and ensure that your heating system operates efficiently and effectively. Remember to consider additional factors and consult with a professional if you're unsure about any aspect of the calculation. Happy calculating!