Excel VBA is a powerful tool for automating tasks in Excel, and using variables to select ranges can make your code more flexible and efficient. In this article, we'll explore how to use variables in Excel VBA range selection.
Why Use Variables in Range Selection?
Using variables in range selection allows you to dynamically change the range of cells that your code interacts with. This can be useful in a variety of situations, such as:
- When you need to perform the same task on different ranges of cells
- When you need to modify your code to work with different worksheets or workbooks
- When you need to make your code more flexible and adaptable to changing data
Declaring Variables for Range Selection
To use variables in range selection, you need to declare the variable and assign it a value. Here's an example:
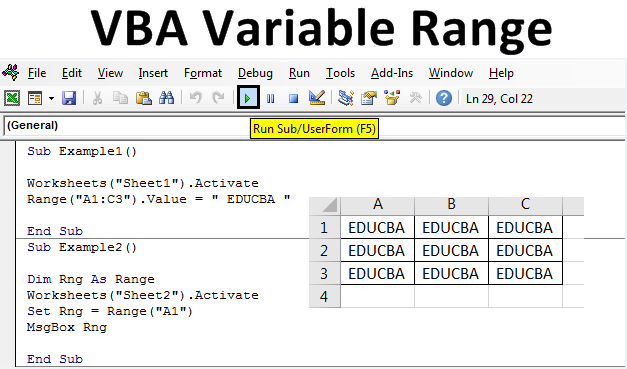
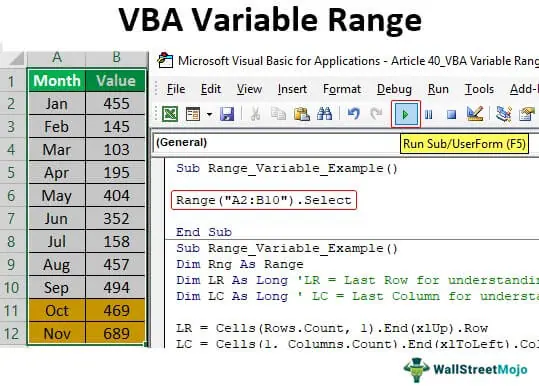
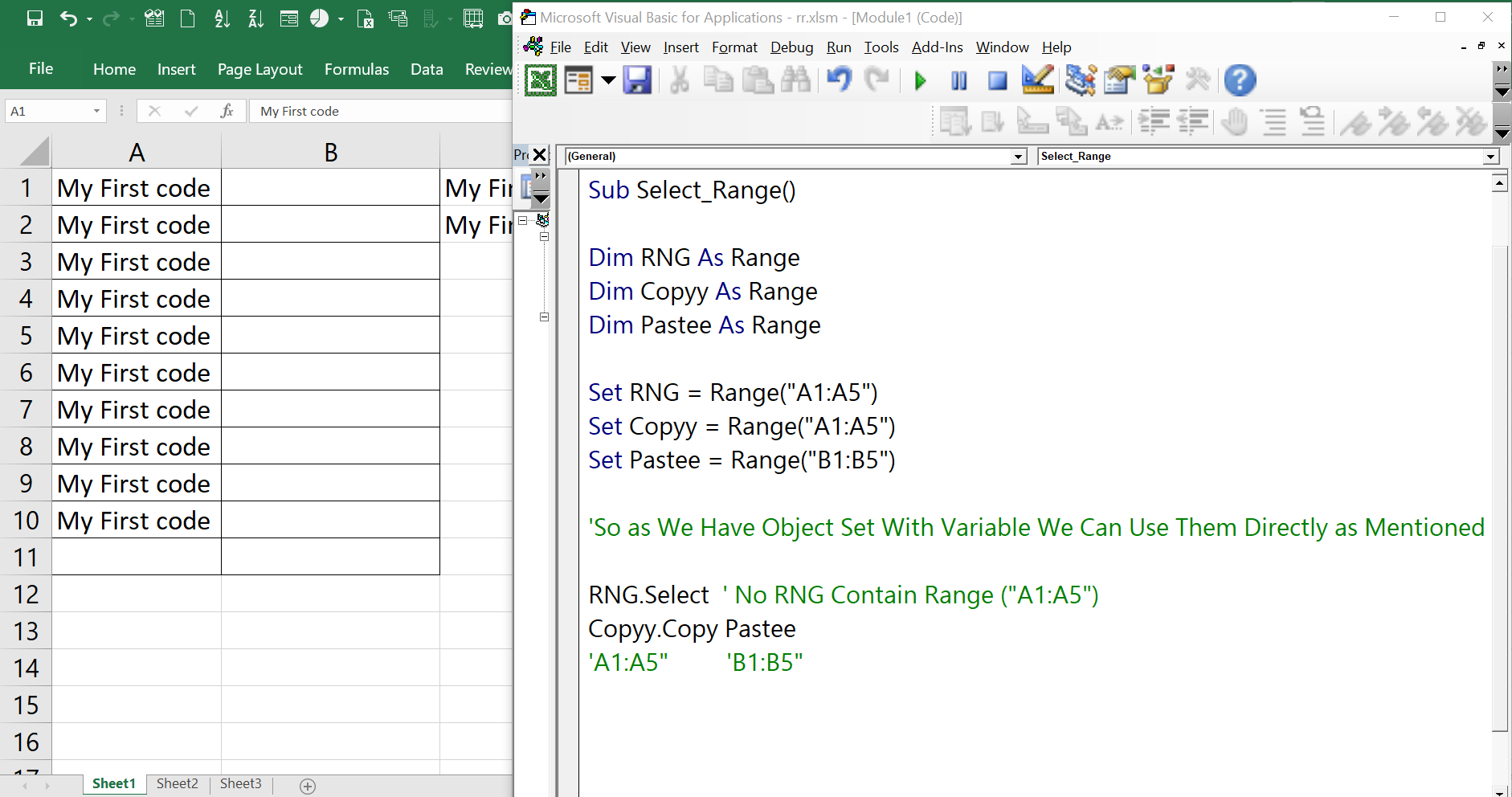
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("A1:B2")
In this example, we declare a variable myRange of type Range and assign it the value of the range A1:B2. We use the Set keyword to assign the value to the variable.
Using Variables in Range Selection
Once you've declared and assigned a value to your variable, you can use it in range selection. Here's an example:
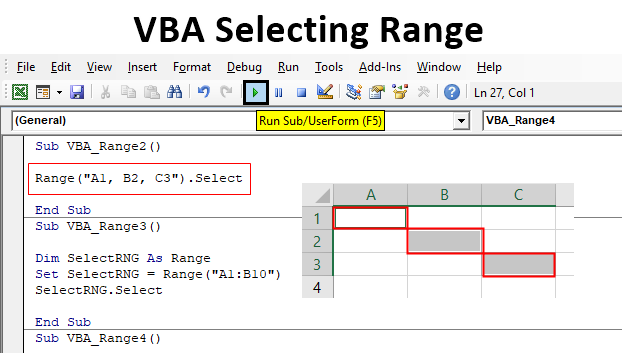
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("A1:B2")
myRange.Select
In this example, we use the myRange variable to select the range of cells. This code will select the cells in the range A1:B2.
Using Variables with Other Range Methods
You can also use variables with other range methods, such as Offset, Resize, and Find. Here are some examples:
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("A1:B2")
myRange.Offset(1, 1).Select
myRange.Resize(3, 3).Select
myRange.Find("Hello").Select
In these examples, we use the Offset, Resize, and Find methods to modify the range of cells that we're working with.
Using Variables with Looping
You can also use variables with looping statements, such as For and While loops. Here's an example:
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = Range("A1:B2")
For i = 1 To 10
myRange.Offset(i, 0).Select
Next i
In this example, we use a For loop to iterate over a range of cells, using the Offset method to move the range down one row each time.
Using Variables with Worksheet and Workbook Objects
You can also use variables with worksheet and workbook objects. Here's an example:
Dim myWorksheet As Worksheet
Set myWorksheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim myRange As Range
Set myRange = myWorksheet.Range("A1:B2")
In this example, we declare a variable myWorksheet of type Worksheet and assign it the value of the worksheet "Sheet1". We then use this variable to set the value of the myRange variable.
Best Practices for Using Variables in Range Selection
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when using variables in range selection:
- Always declare your variables before using them
- Use meaningful variable names to make your code easier to understand
- Use the
Setkeyword to assign values to range variables - Avoid using
Selectstatements whenever possible, as they can slow down your code - Use variables to make your code more flexible and adaptable to changing data
Conclusion
Using variables in Excel VBA range selection can make your code more flexible and efficient. By declaring variables and using them to select ranges, you can write more dynamic and adaptable code that can handle changing data and different worksheets and workbooks.

Gallery of Excel VBA Range Selection




FAQs
What is the benefit of using variables in Excel VBA range selection?
+Using variables in Excel VBA range selection allows you to write more dynamic and adaptable code that can handle changing data and different worksheets and workbooks.
How do I declare a variable in Excel VBA?
+To declare a variable in Excel VBA, use the `Dim` statement followed by the variable name and data type.
What is the difference between `Set` and `Let` in Excel VBA?
+In Excel VBA, `Set` is used to assign a value to a range variable, while `Let` is used to assign a value to a non-range variable.