Are you tired of dealing with the frustrating "Is Blank" error in Excel VBA? This error can be a major roadblock in your workflow, preventing you from completing tasks efficiently. Fortunately, we've got you covered. In this article, we'll walk you through the easy steps to fix the Excel VBA "Is Blank" error, so you can get back to work without any hassle.
Understanding the "Is Blank" Error
Before we dive into the solutions, it's essential to understand what causes the "Is Blank" error. This error typically occurs when you're trying to perform an operation on a cell or range that contains a blank or null value. In VBA, a blank cell is not the same as an empty string, which can lead to unexpected errors.
Step 1: Check for Blank Cells
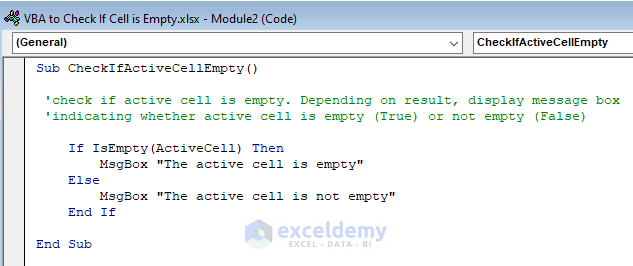
The first step in fixing the "Is Blank" error is to check if the cell or range you're working with contains any blank cells. You can do this by using the IsEmpty function or the ="" operator. Here's an example:
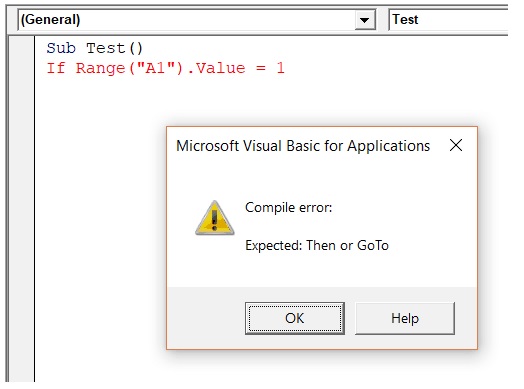
If IsEmpty(Range("A1").Value) Then
MsgBox "Cell A1 is blank"
End If
Alternatively, you can use the ="" operator:
If Range("A1").Value = "" Then
MsgBox "Cell A1 is blank"
End If
Step 2: Use the Trim Function
If you're working with a string variable, you can use the Trim function to remove any leading or trailing spaces. This can help prevent the "Is Blank" error when working with strings. Here's an example:
Dim myString As String
myString = Trim(Range("A1").Value)
Step 3: Use the If Not IsNull Statement
When working with variables that may contain null values, you can use the If Not IsNull statement to check if the variable is not null before performing any operations. Here's an example:
If Not IsNull(Range("A1").Value) Then
' Perform operations on Range("A1").Value
End If
Step 4: Use the If Not IsEmpty Statement
Similar to the previous step, you can use the If Not IsEmpty statement to check if a cell or range is not empty before performing any operations. Here's an example:
If Not IsEmpty(Range("A1").Value) Then
' Perform operations on Range("A1").Value
End If
Step 5: Use the On Error Resume Next Statement
In some cases, you may want to ignore the "Is Blank" error and continue executing your code. You can use the On Error Resume Next statement to achieve this. However, be cautious when using this statement, as it can mask other errors in your code. Here's an example:
On Error Resume Next
' Perform operations on Range("A1").Value
On Error GoTo 0

Step 6: Use the Application.Evaluate Method
In some cases, you may need to evaluate a formula that contains a blank cell. You can use the Application.Evaluate method to evaluate the formula and return a value. Here's an example:
Dim result As Variant
result = Application.Evaluate("=A1+B1")
Step 7: Use the Range.Find Method
If you're searching for a specific value in a range, you can use the Range.Find method to find the value and return a range object. Here's an example:
Dim foundRange As Range
Set foundRange = Range("A1:A10").Find("MyValue")
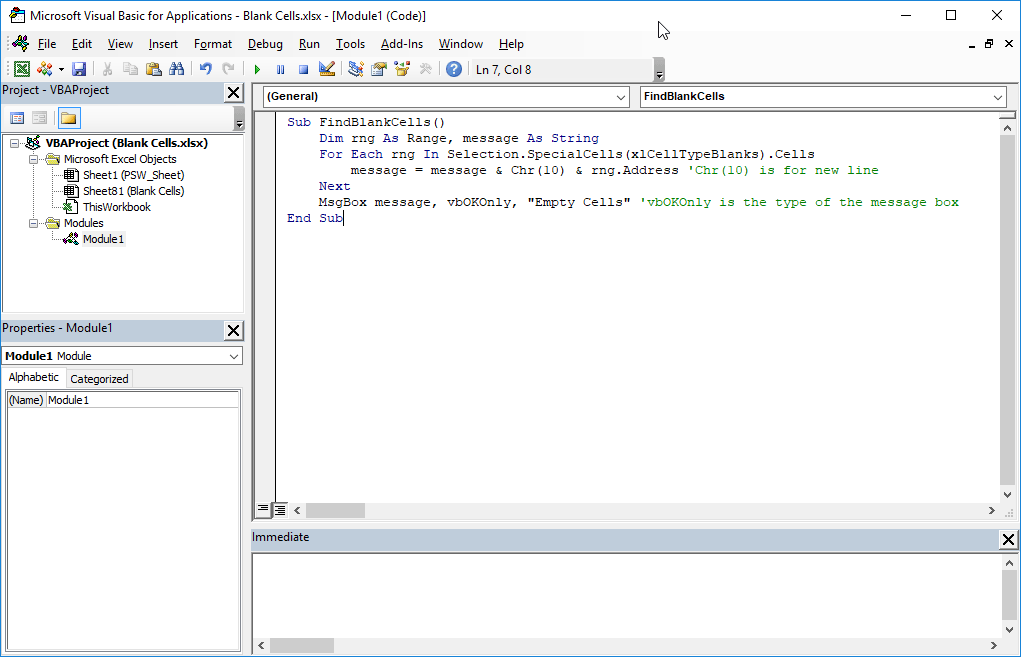
Step 8: Use the Range.SpecialCells Method
You can use the Range.SpecialCells method to find cells that meet specific criteria, such as blank cells. Here's an example:
Dim blankCells As Range
Set blankCells = Range("A1:A10").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
By following these easy steps, you should be able to fix the Excel VBA "Is Blank" error and get back to work without any hassle.
Gallery of Excel VBA Error Fixing




FAQs
What causes the "Is Blank" error in Excel VBA?
+The "Is Blank" error typically occurs when you're trying to perform an operation on a cell or range that contains a blank or null value.
How can I check if a cell is blank in Excel VBA?
+You can use the `IsEmpty` function or the `=""` operator to check if a cell is blank.
What is the difference between `IsEmpty` and `IsNull` in Excel VBA?
+`IsEmpty` checks if a cell is blank, while `IsNull` checks if a variable contains a null value.