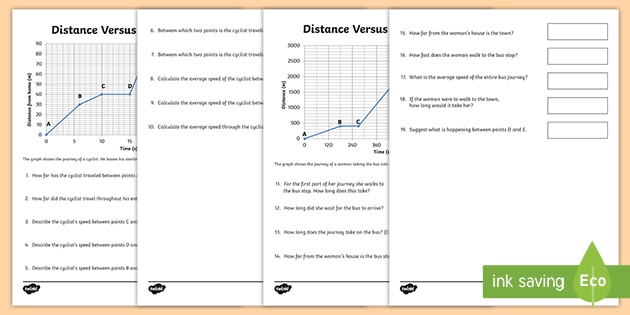
Understanding distance-time graphs is a fundamental concept in physics and mathematics, crucial for students to grasp as they progress in their studies. These graphs provide a visual representation of the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time taken, offering insights into an object's motion, including its speed and velocity. Here's a comprehensive guide to help students work with distance-time graphs, accompanied by a worksheet to practice and reinforce their understanding.
What is a Distance-Time Graph?
A distance-time graph is a graphical representation showing how the distance traveled by an object changes over time. The distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y-axis), and the time is plotted on the horizontal axis (x-axis). These graphs are essential for understanding motion, as they can illustrate if an object is moving at a constant speed, accelerating, or decelerating.
Reading Distance-Time Graphs
To read a distance-time graph, you need to understand what the shape of the graph indicates about the object's motion.
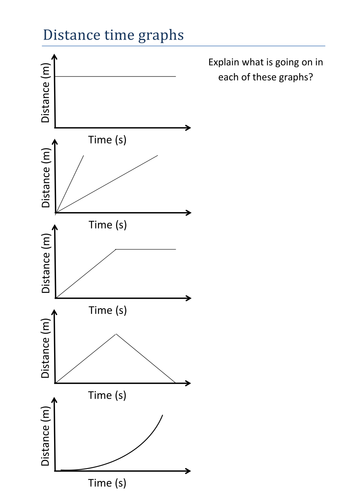
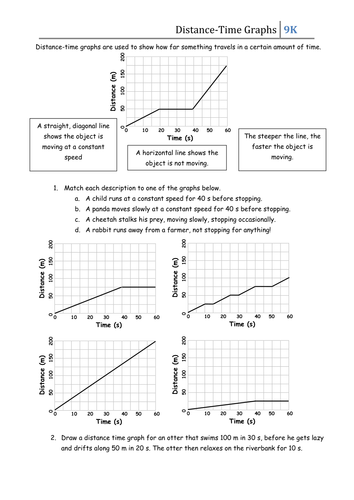
- Straight Line: A straight line indicates that the object is moving at a constant speed. The steeper the line, the faster the object is moving.
- Curved Line: A curved line indicates that the object's speed is changing over time. If the curve is upward, the object is accelerating. If the curve is downward, the object is decelerating.
- Horizontal Line: A horizontal line indicates that the object is not moving (it is at rest).
Interpreting Distance-Time Graphs
Interpreting these graphs involves understanding the information they convey about an object's motion.
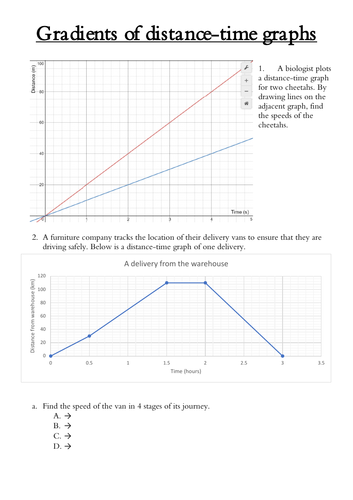
- Speed: The speed of an object can be determined by the steepness of the line on the graph. A steeper line indicates a higher speed.
- Acceleration: Acceleration is indicated by a change in the steepness of the line. If the line becomes steeper over time, the object is accelerating.
- Deceleration: Deceleration is indicated if the line becomes less steep over time.
Worksheet: Distance-Time Graphs
Exercise 1: Identifying Motion
Look at the distance-time graph below and identify the type of motion represented.

a) Is the object moving at a constant speed? b) Is the object accelerating or decelerating? c) What can be said about the object's speed?
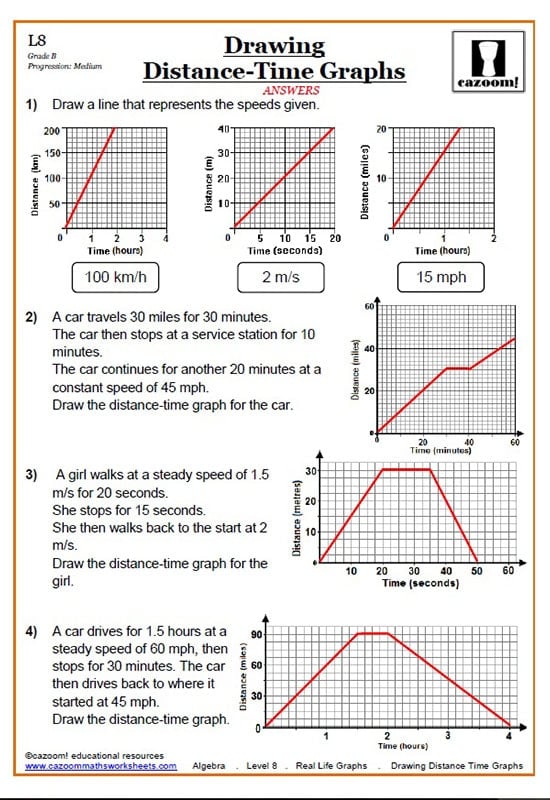
Exercise 2: Drawing Distance-Time Graphs
Draw a distance-time graph for an object that starts from rest, accelerates uniformly to a speed of 10 meters per second in 5 seconds, and then maintains this speed for another 5 seconds.
Exercise 3: Speed and Acceleration
An object moves with a constant speed of 20 meters per second for 10 seconds. Then, it accelerates uniformly to 30 meters per second in 5 seconds.
a) Sketch the distance-time graph for this motion. b) Calculate the acceleration of the object during the 5-second acceleration period.
Exercise 4: Deceleration
An object travels at a speed of 40 meters per second for 10 seconds. Then, it decelerates uniformly to rest in 10 seconds.
a) Sketch the distance-time graph for this motion. b) Calculate the deceleration of the object during the 10-second deceleration period.
Exercise 5: Mixed Motion
An object accelerates from rest to 20 meters per second in 5 seconds, maintains this speed for 10 seconds, decelerates to rest in the next 5 seconds, and then stays at rest for another 10 seconds.
Sketch the distance-time graph for this motion.
Gallery of Distance-Time Graphs




FAQs
What does a horizontal line on a distance-time graph indicate?
+A horizontal line indicates that the object is at rest.
How can you tell if an object is accelerating on a distance-time graph?
+An object is accelerating if the line on the graph becomes steeper over time.
What does the steepness of the line on a distance-time graph represent?
+The steepness of the line represents the speed of the object. A steeper line indicates a higher speed.
Understanding distance-time graphs is crucial for analyzing motion in physics. By practicing with the exercises provided, students can gain a deeper understanding of how to read, interpret, and sketch these graphs, which will aid in their comprehension of more complex physics concepts.